B400M on DAHDI User Manual
Contents
2.4 Adjusting Termination of S/T Interface (100 ohm)
Chapter 3 Software Installation and Configuration
General Safety Instructions
CAUTION
1. The computers that have B400M card installed must comply with
the country’s specific safety regulations.
- Only service personnel should install B400M card.
- Before you install B400M card, please unplug the power cord from the computer and remove the cover from your PC.
- For avoiding personal injuries and damage to your computer and
B400M card, make sure bracket of the card is secured to the PC’s chassis ground by fastening the card with screws.
- Electrical Surges, ESD are very destructive to the equipment. To avoid it, make sure there is a low impedance discharge path from your computer to chassis ground.
- To reduce the risk of damage or injury, please follow all steps or procedures as instructed.
Test Environments
CentOS-5.6
Kernel version: 2.6.18-238.12.1.el5
DAHDI: dahdi-linux-complete-2.4.1.2+2.4.1
Asterisk: 1.8.5.0
Libpri: 1.4.11.5
Hardware: OpenVox B400M
Chapter 1 Overview
1.1 What is Asterisk
The Definition of Asterisk is described as follows:
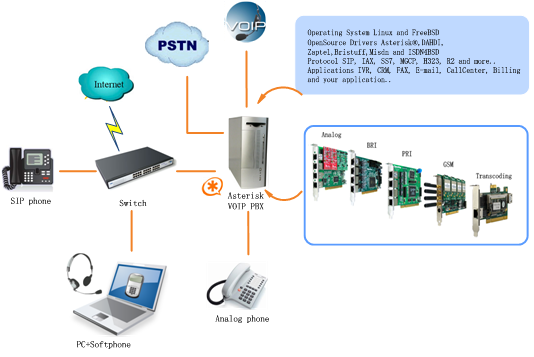
Asterisk is a complete PBX in software. It runs on Linux, BSD, Windows (emulated) and provides all of the features you would expect from a PBX and more. Asterisk does voice over IP in four protocols, and can interoperate with almost all standard-based telephony equipments using relatively cost-effective hardware. Asterisk provides Voicemail services with Directory, Call Conferencing, Interactive Voice Response, and Call Queuing. It supports three-way calling, caller ID services, ADSI, IAX, SIP, H323 (as both client and gateway), MGCP (call manager only) and SCCP/Skinny (voip-info.org).
Figure 1 Topology
1.2 What is B400M
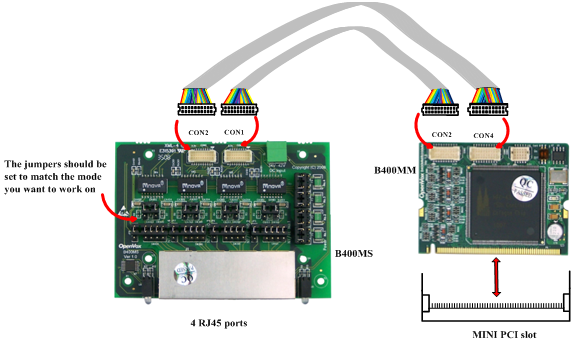
OpenVox B400M is a Mini PCI type III BRI card which supports 4 BRI S/T interface. All 4 BRI ports can be configured for TE or NT mode individually by jumpers. This port configuration is detected by the driver automatically.
The B400M consists of two parts: the B400MM and the B400MS. The B400MM connects Mini PCI slot while the B400MS provides S/T BRI interface connection.B400M S/T BRI interface card delivers great voice quality in the telephony systems. It can provide 8 simultaneous voices calls over 4 ISDN BRI line, turns your legacy ISDN BRI equipments into powerful Voice over IP devices and provides a soft migration path from ISDN technology to the new Voice over IP world. B400M is designed for building Open Source systems based on Asterisk such as ISDN PBX and VoIP gateway. The B400M and drivers comply with fully GPLed for the Linux kernel bring powerful ISDN BRI connectivity to your Linux machine.
B400M works well with Asterisk®, Elastix®, FreeSWITCH™, PBX in a Flash, trixbox®, Yate™ and IPPBX/IVR projects as well as other Open Source and proprietary PBX, Switch, IVR, and VoIP gateway applications.
Target applications
- High Performance ISDN PC Cards
- ISDN PABX for BRI
- VoIP Gateways
- ISDN LAN Routers for BRI
- ISDN Least Cost Routers for BRI
- ISDN Test Equipment for BRI
Main features
- Up to 4 ports of S/T interfaces, support Mini PCI type III
- ITU-T I.430 and TBR 3 certified and S/T ISDN supporting TE/NT mode
- Design for low power systems
- DTMF detection on all B-channels
- Multiparty audio conferences bridge
- Each of the 4 ports can be independently configured for TE or NT mode
- Full software and hardware compatible with Junghanns.NET ISDN, mISDN driver, DADHI and so on.
- RoHS compliant
- Certificates: CE, FCC, A-Tick
- trixbox TM Officially Certified
- Elastix® Officially Certified
Chapter 2 Hardware Setup
There are some points should be paid attention to when setting up B400M.
2.1 Power supply
The board is powered by Mini PCI slot which provides +3.3V, it works well on TE mode; but if you need to use NT mode, a power supply converter named PFM100 is necessary to apply together, which can be used for NT mode of B100M/B200M/B400M. More information about PFM100 please refers to HERE.
2.2 Slot compatibility
B400M is compatible with 32-bit 3.3V Mini PCI type III slot.
Figure 2 124 pin Mini-PCI Type III (Amp 1318228-1) connector
The Mini PCI specification uses a subset of the PCI signal set. Mini-PCI is a small form factor version of a PCI card. The Mini-PCI bus only uses 3.3 volts and the 32-bit PCI bus. Mini PCI type III slot is a 124-pin connector used with Type III Mini-PCI cards. The 124-Pin connector accepts a card edge and a board with fingers.
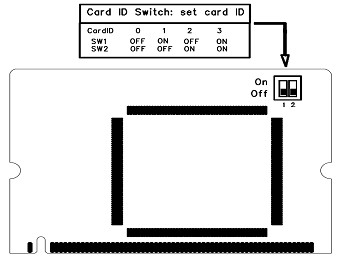
2.3 Setting Card ID
If want to install more than one card of B400M in a PC, you should take care of the card ID switch. The state of ON stands for "1"in binary, OFF represents "0", and Card ID is calculated by binary. For instance, the two switches should be all set to OFF if there is only one card, which means their corresponding binary value is "00" and the decimal number is "0". There two pieces of rules you must obey to set Card ID:
- The ID of the first card must be set to 0, and the second should be set to 1, and so forth.
- The first card is a card that will be initialized (i.e. installing driver) firstly when the system boot up. At most cases, Linux will initialize PCI devices according to their slot order. The slot nearest to the CPU will be initialized firstly and the far end slot will be initialized at last. That is to say, the card which is nearest to the CPU ID should be set to 0 if there are more than one B400M on your machine.
Figure 3 Card ID Setting
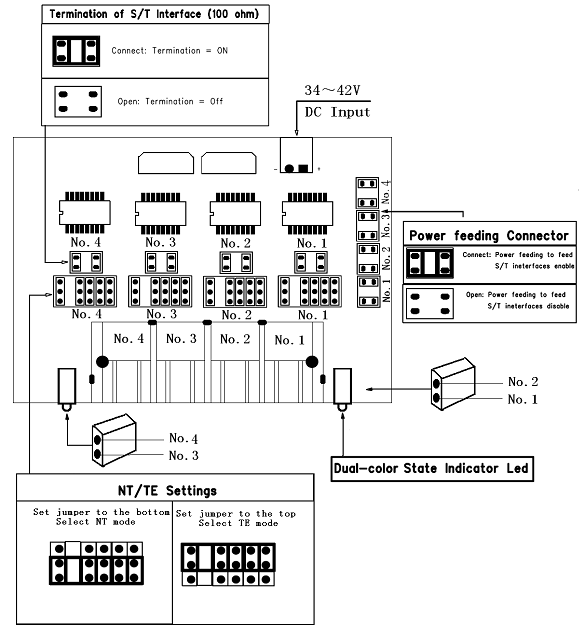
2.4 Adjusting Termination of S/T Interface (100 ohm)
You are able to set a port to NT or TE mode, please refer to figure 4 for visualized information.
- If a port works on NT mode, you should set jumper to CONNECT (ON).
- If a port works on TE mode, theoretically it should be set to OPEN (OFF), but it might connect to some non-standard ISDN terminal equipments that do not have terminal resistors, for such equipments, you should set it to CONNECT(ON).
- Use the connection cable to connect B400MM and B400MS. On the B400MM, there are two slots for RJ45 expansion board; the two slots are used to connect the slots on B400MS. The connection should be:
Figure 4 Cable connector
Caution: As figure 4 shows, CON2 of B400MM controls channel 1 and channel 2 of B400MS, CON4 of B400MM controls channel 3 and channel 4 of B400MS, so it is channel3, channel 4, channel 1, channel 2 from left to right side in figure 4. But if you connect CON2 on B400MS to CON2 on B400MM and connect CON1 to CON4, it is channel 1, channel 2, channel 3, and channel 4 from left to right side.
2.5 Power Feeding Connector
These jumpers control whether the card will feed power to the external isdn terminal. User should adjust accordingly from the following:
- If the port works on TE mode, user MUST set the jumper to OPEN(OFF)
- If this port works on NT mode, and the ISDN terminal requires ISDN power supply, users should set the jumper to CONNECT (ON), and also need an accessory named PFM100, Please refer to HERE.
While ISDN terminal does not require ISDN power supply, users should set the jumper to OPEN (OFF).
Figure 5 Jumper Setting
2.6 Hardware setup procedure
- Power off your PC, remember to unplug the AC power cable
- Set card ID as previously stated if there are more than one BRI card and set the jumpers on right.
- Insert B400MM into a Mini PCI slot
- If need power for external equipments, please refer to the jumper setting section for more details.
- Plug ISDN lines into RJ-45 interfaces which set as TE mode and ISDN phone lines into RJ-45 interface which set as NT mode
- Fix the board by screws
- Plug back the AC power cable, and power on PC
Caution: During the above processes, an ESD wrist strap is needed. Once power is on, you must not attempt to install or take down the board. After hardware setup appropriately, it is time to install software.
Chapter 3 Software Installation and Configuration
B400M supports DAHDI software driver on Linux. To make full use of B400M, you should download, compile, install and configure DAHDI, Libpri and Asterisk. Let’s make specific versions for an example to state how to install software.
3.1 Download
DAHDI software packages are available on OpenVox official website or Digium. Some patches should be applied when the driver source is from Digium. Therefore, it is recommended that downloading the DAHDI driver package from OpenVox official website.
Gain DAHDI source package from OpenVox:
Get Libpri and Asterisk software packages from Digium official website:
http://downloads.asterisk.org/pub/telephony/libpri/releases/libpri-1.4.11.5.tar.gz
http://downloads.asterisk.org/pub/telephony/asterisk/releases/asterisk-1.8.5.0.tar.gz
Execute the following commands under the directory of /usr/src/ in generally to download and decompress these packages:
#_wget_http://downloads.asterisk.org/pub/telephony/libpri/releases/libpri-1.4.11.5.tar.gz
# tar -zxvf libpri-1.4.11.5.tar.gz
# tar -zxvf dahdi-linux-complete-current.tar.gz
#_wget_http://downloads.asterisk.org/pub/telephony/asterisk/releases/asterisk-1.8.5.0.tar.gz
# tar -zxvf asterisk-1.8.5.0.tar.gz
Also you can get the DAHDI source code from Digium official website:
# tar -zxvf dahdi-linux-complete-2.4.1.2+2.4.1.tar.gz
- If using Asterisk 1.8, it is not need to make any patches more.
- If using Asterisk 1.6, please modify the file: asterisk-1.6.xx/channels/chan_dahdi.c.
Please comment out the following line:
Then add the following two lines after the above action:
3.2 Installation
1. Hardware detection
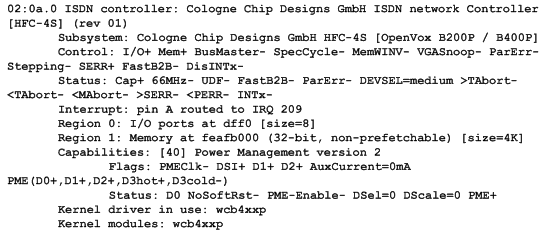
# lspci –vvvv
Check the outcome and confirm your system has recognized B400M. If it has been recognized, "ISDN controller" will be displayed in the output information like that:
Figure 6 Hardware detection
If B400M is not recognized by the system, you have to cut the server power off, take out the card to clean the slot and insert it into the mini PCI slot again.
2. Software installation
Some dependencies are crucial. If any of them is absent, the software installation process would not go through successfully. Let’s run "yum install XX" (XX stands for the dependency’s name) to check the availability of dependencies.
# yum install bison
# yum install bison-devel
# yum install ncurses
# yum install ncurses-devel
# yum install zlib
# yum install zlib-devel
# yum install openssl
# yum install openssl-devel
# yum install gnutls-devel
# yum install gcc
# yum install gcc-c++
# yum install libxml2
# yum install libxml2-devel
If there is no kernel source in the system, you should also install it by running like:
# yum install kernel-devel
If the dependency has been installed, system will indicate that nothing to do, which means you could go to next one directly. Otherwise, the system will keep on installing it.
Change to the directory of dahdi-linux-complete-XX (XX represents DAHDI version), then perform commands one by one to install DAHDI.
# cd /usr/src/dahdi-linux-complete-2.4.1.2+2.4.1
# make
# make install
# make config
Caution: If there is something wrong after "make", please refer to HERE. In the url link, the moderator introduces you a method how to patch. After patching, save your changes and exit. Then run "make" again, if successfully done, it is time for you to install Libpri and Asterisk.
Please execute those commands to install Libpri and Asterisk:
# cd libpri-1.4.11.5
# make
# make install
# cd asterisk-1.8.5.0
# ./configure
# make
# make install
# make samples
"make samples" will install the standard sample configuration file in the directory /etc/asterisk. As a freshman, you should perform "make samples", that is to say, it is unnecessary to perform "make samples" every time. Because once performed, it will cover the old sample configuration files you have installed.
3.3 Configuration
1. Driver loading
After compiling and installing DAHDI, Libpri and Asterisk, please load the driver by running commands:
# modprobe dahdi
# modprobe wcb4xxp
# dahdi_genconf
# dahdi_cfg -vvv
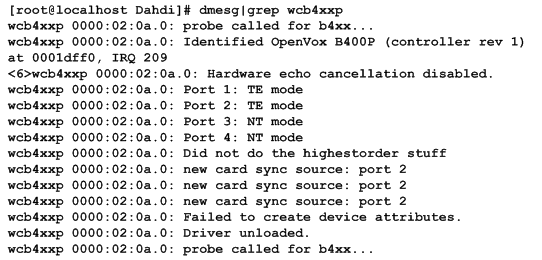
OpenVox B400M has great adaptive ability that it can be set as TE/NT mode automatically without any parameters. When the driver module "wcb4xxp" loaded, B400M card will be set as specific mode just depending on the hardware jumper settings. You can see the messages when execute a command below:
# dmesg|grep wcb4xxp
Figure 7 dmesg information
After running "modprobe dahdi" or "modprobe wcb4xxp", there is not any information displayed if loaded normally and successfully. "wcb4xxp" is the driver module name of B400M.
If there is any error, please trace the cause. Until all errors are clear up, you could execute "dahdi_genconf" again, and then go to the next step. By running "dahdi_genconf", it will generate /etc/dahdi/system.conf and etc/asterisk/dahdi-channels.conf automatically. Checking whether the generated files information agrees with your hardware setup, if not, you should modify to your specific requirements. Do not forget to confirm that dahdi-channels.conf is included in chan_dahdi.conf, if not, run command:
# echo "#include dahdi-channels.conf" >> /etc/asterisk/chan_dahdi.conf
A part of system.conf which is one of the basic configuration files is displayed as follows:
Figure 8 A part of system.conf
2. Country mode modification
In order to match your country mode, it is need to change parameters loadzone and defaultzone to your country. For example, your system is inCHINA, you would like them change to:
loadzone = cn
defaultzone = cn
Some zonedata is available in the file
../dahdi-XX/tools/zonedata.c, you can refer to it to match your country mode. Meanwhile, you also need to modify another parameter which is in file /etc/asterisk/indications.conf.
country=cn
A part of file /etc/asterisk/dahdi-channels.conf is showed as below. (Modification, if it is not agree with the hardware setup. Here is an example that assumes port 1& 2 are set to TE mode, port 3& 4 are set to NT mode.)
Figure 9 A part of dahdi-channels.conf
3. Asterisk initiation
Execute a command to start Asterisk:
# asterisk -vvvvvvgc
If Asterisk is already activate, run "asterisk –r" instead.
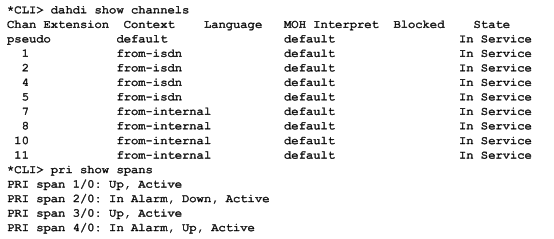
In the CLI, please run the following commands
"dahdi show channels" and "pri show spans":
Figure 10 channels and spans show
If you can see the span is up, active and not "In Alarm”, it means successful installation. Otherwise, please check the configuration files and physical connections.
4. Dialplan edit
You should make sure that the context "from-isdn" and "from-internal" are in extensions.conf. Here a simple example is given:
# vim /etc/asterisk/extensions.conf
Figure 11 dial plan
After saving your dialplan, please run "asterisk –r", then execute "reload" in the CLI. Now you are able to make calls. The above dialplan achieves that:
- If there is a call from the ISDN line, Asterisk will transfer to SIP extension 100, then the SIP phone rings;
- If SIP extension 100 dials any phone number, Asterisk will transfer to the destination phone through the first channel.
- If SIP extension 100 dials any channel number, Asterisk will transfer to the destination ISDN phone which connects to the channel.
Chapter 4 Reference
Tips
Any questions during installation please consult in our forum or look up for answers from the following websites:
Appendix A Specifications
• Weight and size
Weight: B400MM:16g (0.56oz)
B400MS: 44g (1.55oz)
Size: B400MM:5.9×4.4×0.7cm (2.32×1.73×0.28 inch)
B400MS:9.6×6.9×1.4cm (3.78×2.72×0.55 inch)
• Interfaces
3.3V Mini PCI type III
LocalLoopAccess: RJ-45 ports used on certain ISDN S/T/U interfaces
• Environment
Temperature: 0 ~50°C (Operation) - 40 ~125°C (Storage)
Humidity: 10 ~90% NON-CONDENSING
• Power consumption
Voltage: 3.3V/ 38V (NT only)
Power Dissipation Max:0.7W/8.8W
• Hardware and software requirements
RAM 32 + MB CPU 200+ MHZ
Linux kernel 2.6.X
Appendix B PIN Assignments
Basic Rate ISDN lines can use straight ("flat") modular cable if necessary. However, twisted-pair are more common.
l ISDN U-interface
8-pin RJ45 port | PIN | Color | Description |
1 | White/Orange | N/A | |
2 | Orange | N/A | |
3 | White/Green | N/A | |
4 | Blue | U interface | |
5 | White/Blue | U interface | |
6 | Green | N/A | |
7 | White/Brown | -48VDC Power (optional) | |
8 | Brown | -48VDC Return (optional) |
The U-Interface is most commonly used in North American Basic Rate ISDN systems. The U-Interface is an 8-conductor, modular, RJ-45 jack. The center two pins (pin 4 and 5) are used for the 2-wire loop. The wiring of pin 4 and pin 5 are not polarity sensitive (e.g. 4 and 5 may be crossed).
Optional -48 VDC power may be utilized on RJ-45 pins 7 and 8. This can be used to power the NT-1 and TE equipments if sufficient power is available. In most cases, power is not provided from the telephone company.
l BRI S-Interface
8-pin RJ45 port | PIN | Color | Description |
1 | White/Orange | N/A | |
2 | Orange | N/A | |
3 | White/Green | Receive+ | |
4 | Blue | Transmit + | |
5 | White/Blue | Transmit - | |
6 | Green | Receive - | |
7 | White/Brown | -48VDC Power(optional) | |
8 | Brown | -48VDC Return (optional) |
The BRI S-Interface is a 4-wire interface, with separate Transmit and Receive pairs. It can be operated in four modes:
- Point-to-Point Mode allows one logical terminal that may be up to 1 KM from the NT-1
- Short Passive Bus Mode allows connection of up to 8 terminals in parallel on the S/T bus. The terminals can be within 100 to 200 meters from the NT-1.
- Extended Passive Bus Mode allows connection to 8 terminals at distances of up to 500 meters from the NT-1.
- Star Bus Mode allows interconnection of up to 8 terminals to a central NT-1. Each terminal can be up to 1 KM from the NT-1.
² The NT-1 unit has configurable jumpers to apply a 100-ohm termination to the S-Interface signal pairs. Usually, these jumpers will be in. Rules of termination is similar to that of the SCSI-bus: the NT-1 will have 100-ohm terminators applied, and the farthest TE1/TA device will have 100-ohm terminators.
² Optional power to the NT-1 can be applied from pins 7 and 8 of the S-Interface RJ-45 jack. This is usually not used.
² Many NT-1 units provide "phantom-power" (sealing current) between the transmit (4,5) and receive (3,6) leads. In these cases, the Transmit (4,5) leads will be negative with respect to the Receive (3,6) leads. This is often selectable in the NT-1. Whenever possible, it is recommended that this option be disabled. As a general rule-of-thumb, most PC cards, routers, and other data communications equipment do not require power from the S/T interface. ISDN telephones usually require power from the S/T interface.
² Most NT-1 units will ship with a wall-mount transformer power supply for the NT-1.