DGW-L1 User Manual
1. Overview
What is DGW-L1?
OpenVox T1/E1 Gateway is an open source asterisk-based VoIP Gateway solution for operators and call centers. It is a converged media gateway product. This kind of gateway connects traditional telephone system to IP networks and integrates VoIP PBX with the PSTN seamlessly. With friendly GUI, users may easily setup their customized Gateway. Also secondary development can be completed through AMI (Asterisk Management Interface). The DGW-L1 could support 12v power supply.
It is developed with a wide selection of codecs and signaling protocol, including G.711A, G.711U, G.729, G.722, G.723 and GSM. It supports PRI/SS7/R2 protocol. OpenVox T1/E1 Gateway has good processing ability and stability. The T1/E1 gateway will be 100% compatible with Asterisk, Elastix, trixbox, 3CX, FreeSWITCH SIP server and VOS VoIP operating platform.
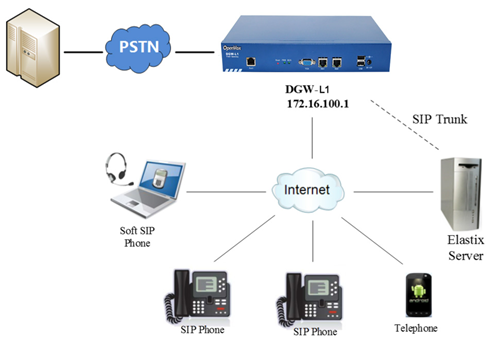
Sample Application
Figure 1-2-1Topological Graph
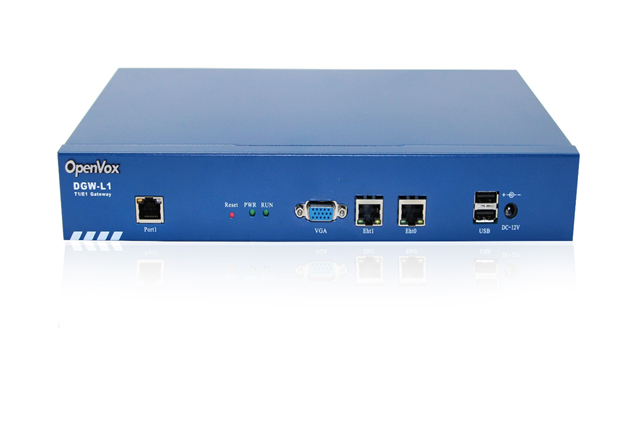
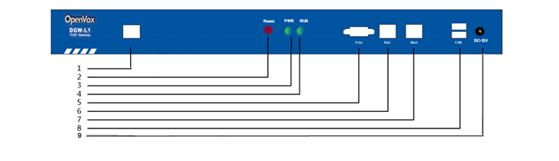
Product Appearance
The picture below is appearance of DGW-L1.
Figure 1-3-1 Product Appearance
Figure 1-3-2 Front Panel
Table 1-3-1 Description of Front Panel
Interface | Function | Color | Work Status |
1 Port | E1/T1 port. There is only one port. | ||
2 Reset | Reset button is used to restore the device. | ||
3 RUN | Register indicator | Green | Slow blinking(Green 2s and Flash 0.1s):Work normally |
Fast blinking(Green 0.5s and Flash 0.5s): Work abnormally | |||
Crazily blinking(Green 0.1s and Flash 0.1s): Preparing restore the device | |||
No blinking: Dahdi Error | |||
4 PWR | Power Status indicator | Green | On: Power is on |
Off: Power is off | |||
5 VGA | VGA monitor connector | ||
6 Eth1 | Network interface | ||
7 Eth0 | Network interface | ||
8 USB | USB interface | ||
9 DC-12v | Power supply |
Main Features
- Based on AsteriskR
- Editable AsteriskRconfiguration file
- Wide selection of codecs and signaling protocol
- Support 512 routing rules and flexible routing settings
- Stable performance, flexible dialing, friendly GUI
- Codecs support: G.711A, G.711U, G.729, G.723, G.722,GSM
- Support ports group management
- Connect legacy PBX systems to low-cost VoIP services
- Connect legacy PBX systems to remote sites over private VoIP links
- Connect IP PBX systems to legacy TDM services
Physical Information
Table 1-5-1 Description of Physical Information
Weight | 1314g |
Size | 31cm*17cm*5cm |
Temperature | -40~85°C (Storage) |
0~40°C (Operation) | |
Operation humidity | 5%~95% non-condensing |
Max power | 12W |
LAN port | 1 |
WAN port | 1 |
Software
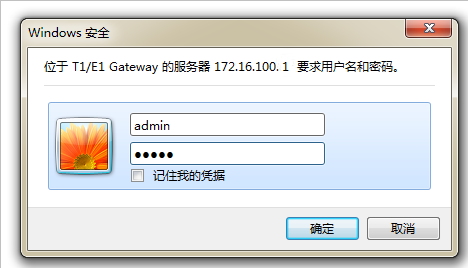
Default IP: 172.16.100.1(Eth0),192.168.100.1(Eth1)
Username: admin
Password: admin
Notice: Log in
Figure 1-6-1 LOG IN Interface
2. System
Status
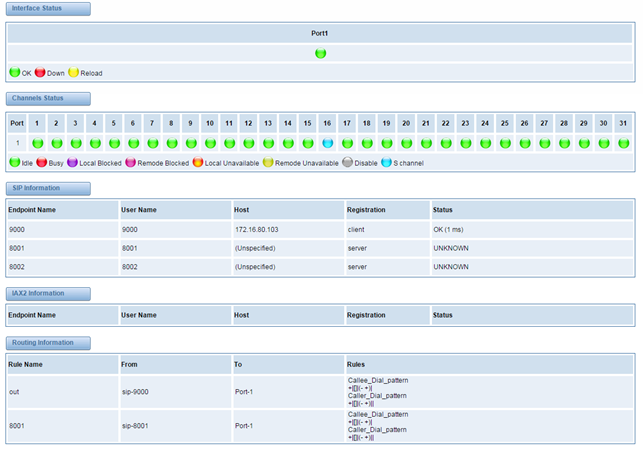
On the “Status” page, you will find all Interface, Status, Time, Login Settings, General, Auto Provision, Tools and Information.
Figure 2-1-1 System Status
Table 2-1-1 Description of System Status
Options | Definition |
Interface Status | Show the status of port, include "RED" and "OK". "RED" means no trunk line connected; "OK" means the trunk line of port is available. |
Signaling Status | Show the signaling status of port, include "Down" and "UP". "Down" means it is unavailable; "UP" means the port is available. |
Time
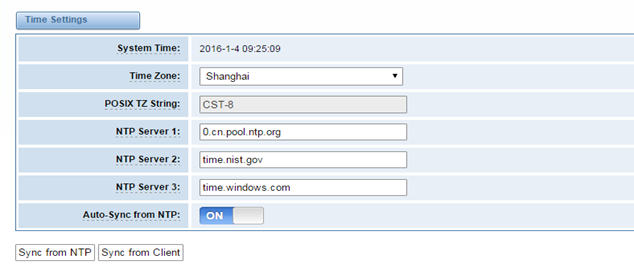
Table 2-2-1Description of Time Settings
Options | Definition |
System Time | Your gateway system time. |
Time Zone | The world time zone. Please select the one which is the same or the closest as your city. |
POSIX TZ String | Posix timezone strings. |
NTP Server 1 | Time server domain or hostname. For example, [time.asia.apple.com]. |
NTP Server 2 | The first reserved NTP server. For example, [time.windows.com]. |
NTP Server 3 | The second reserved NTP server. For example, [time.nist.gov]. |
Auto-Sync from NTP | Whether enable automatically synchronize from NTP server or not. ON is enable, OFF is disable this function. |
Sync from NTP | Sync time from NTP server. |
Sync from Client | Sync time from local machine. |
For example, you can configure like this:
Figure 2-2-1 Time Settings
You can set your gateway time Sync from NTP or Sync from Client by pressing different buttons.
Login Settings
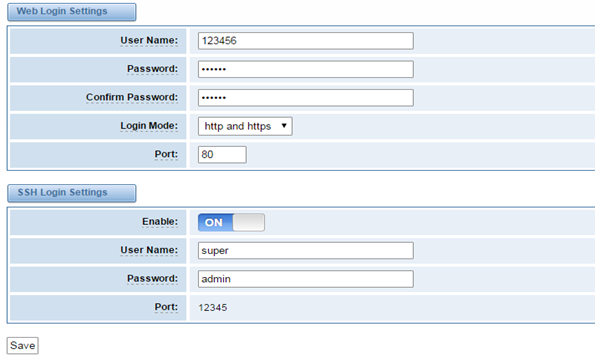
Your gateway doesn't have administration role. All you can do here is to reset what new username and password to manage your gateway. And it has all privileges to operate your gateway. You can modify “Web Login Settings” and “SSH Login Settings”. If you have changed these settings, you don’t need to log out, just rewriting your new user name and password will be OK. Also you can specify the web server port number.
Table 2-3-1Description of Login Settings
Options | Definition | |
User Name |
| |
Password | Allowed characters "-_+. <>&0-9a-zA-Z". Length: 4-32 characters. | |
Confirm Password | Please input the same password as 'Password' above. | |
Port | Specify the web server port number. |
Figure 2-3-1 Login Settings
Notice: Whenever you do some changes, do not forget to save your configuration.
General
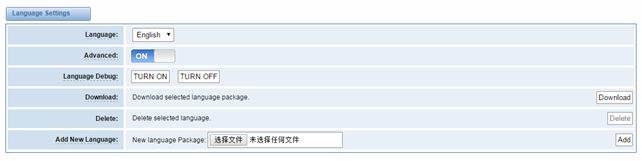
Language Settings
You can choose different languages for your system. If you want to change language, you can switch “Advanced” on, then “Download” your current language package. After that, you can modify the package with the language you need. Then upload your modified packages, “Choose File” and “Add”.
Figure 2-4-1 Language Settings
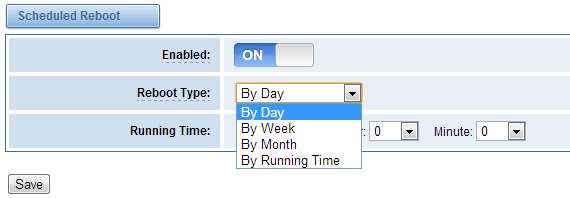
Scheduled Reboot
If switch it on, you can manage your gateway to reboot automatically as you like. There are four reboot types for you to choose, “By Day, By Week, By Month and By Running Time”.
Figure 2-4-2 Reboot Types
If use your system frequently, you can set this enable, it can helps system work more efficient.
Tools and Information
On the “Tools” pages, there are reboot Tools, update Firmware, upload Configuration, backup Configuration and Restore Configuration toolkits.
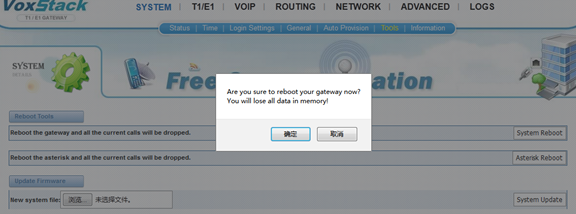
Reboot Tools
You can choose system reboot and Asterisk reboot separately.
Figure 2-6-1 Reboot Prompt
If you press “OK”, your system will reboot and all current calls will be dropped. Asterisk Reboot is the same.
Table 2-6-1 Instruction of reboots
Options | Definition | ||||
System Reboot |
| ||||
Asterisk Reboot | This will restart Asterisk and drop all current calls. | ||||
Update Firmware
We offer 2 kinds of update types for you, you can choose System Update or System Online Update. System Online Update is an easier way to update your system, if you choose that, you will see some information below.
Figure 2-6-2Prompt Information
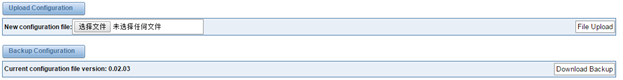
Upload and Backup Configuration
If you want to update your system and remain your previous configuration, you can first backup configuration, then you can upload configuration directly. That will be very convenient for you.
Figure 2-6-3 Upload and Backup
Restore Configuration
Sometimes there is something wrong with your gateway that you don’t know how to solve it, mostly you will select factory reset. Then you just need to press a button, your gateway will be reset to the factory status.
Figure 2-6-4 Factory Reset
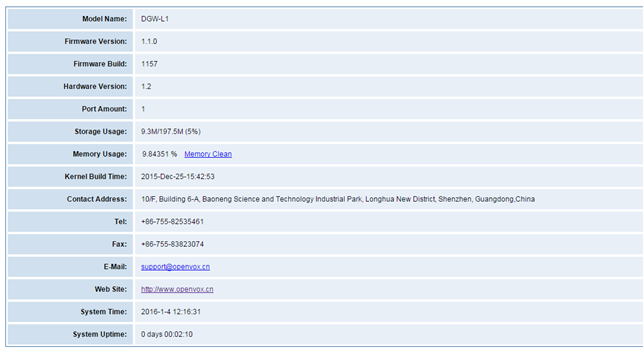
Information
On the “Information” page, there shows some basic information about the T1/E1 gateway. You can see software and hardware version, storage usage, memory usage and some help information.
Figure 2-6-5 System Information
3. T1/E1
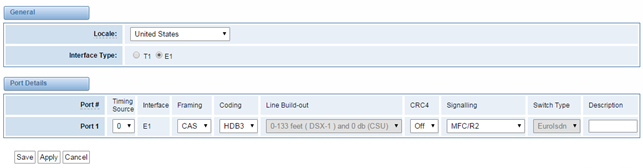
General
Figure 3-1-1 General Settings
Table 3-1-1 Definition of General Settings
Options | Definition |
Local | Your locale. This will be used for the tone style used when in-call indications need to be generated such as ring back, busy, congestion, and other call-oriented inband tone signals. |
Figure 3-1-2 Port Details
Table 3-1-3 Definition of Port Details
Options | Definition |
Timing Source | Timing Source indicate the ports as to which should be used to recover the clock.(0 for master mode, upper for client mode, small number have higher priority ) |
Interface | Choose a line type for this interface, all ports must be the same type. |
Framing | Framing method for this interface |
Coding | Coding method for this interface |
Line Build-out | Line build-out represents the length of the cable form the port on this gateway to the next device. |
CRC4 | Enable cyclic redundancy checking for error checking on line. CRC-4 support is required for all network switches in Europe, but many older switches and PBXs don’t support it. |
Signaling | It shows you what signaling the port uses. |
Switch Type | Only used for PRI |
Description | An optional description of this interface to be used for reference only. |
ISDN-PRI
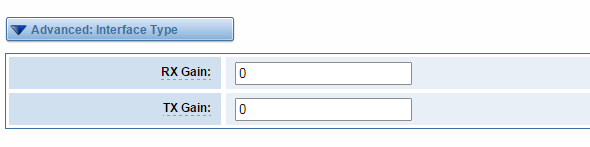
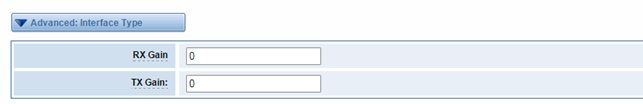
Advanced: Interface Type
Figure 3-2-1 Advanced: Interface Type
Table 3-2-1Definition of Interface Type
Options | Definition |
RX Gain | Gain for the rx channel.Default:0.0 |
TX Gain | Gain for the tx channel.Default:0. |
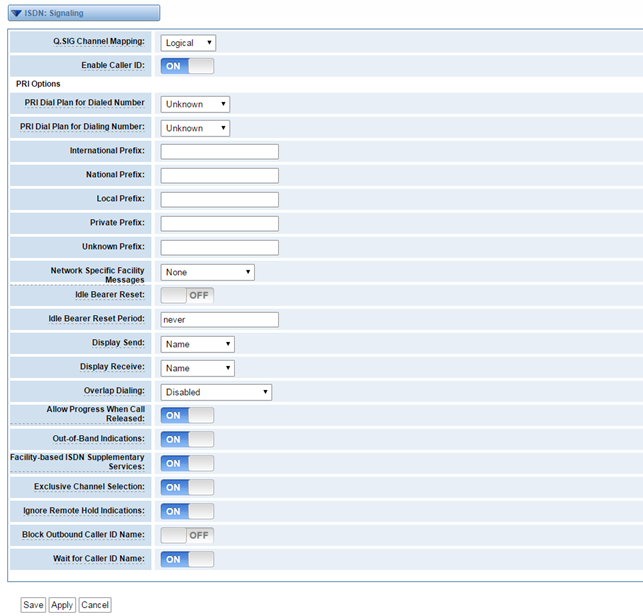
ISDN: Signaling
Figure 3-2-2 ISDN: Signaling
Table 3-2-2 Definition of Signaling
Options | Definition |
Q.SIG Channel Mapping | Sets logical or physical channel mapping. In logical channel mapping, channels are mapped to 1-30. In physical channel mapping, channels are mapped to 1-15, 17-31, skipping the number used for the data channel. Default is physical. |
Enable Caller ID | Whether or not to enable caller ID. |
PRI Dial Plan for Dialed Number | PRI Dialplan: The ISDN_level Type Of Number or numbering plan, used for the dialed number. Leaving this as ‘unknown’ works for most case. In some very unusual circumstances, you may need to set this to ‘dynamic’ or ‘redundant’. |
PRI Dial Plan for Dialing Number | PRI Local Dialplan: Only RARELY used for PRI(sets the calling numbre's numbering plan). In North America, the typical use is sending the 10 digit; callerID number and setting the prilocaldialplan to 'national' (the default); Only VERY rarely will you need to change this. |
Network Specific Facility (NSF) Messages | Some switches (AT&T especially) require network specific facility IE supported values are currently 'none', 'sdn', 'megacom', 'tollfreemegacom', 'accunet' |
Idle Bearer Reset | Whether or not to reset unused B channels. |
Idle Bearer Reset Period | Time in seconds between reset of unused B channels. |
Display Send | Send /receive ISDN display IE option. The display option are a comma separated list of the following option: Block: Do not pass display text data. Name_initial: Use display text in SETUP/CONNECT messages as the party name. Name_update: Use display text in other messages NOTIFY/FACLITY for CLOP name update. Name: Combined name_initial and name_update options. Text: Pass any unused display text data as an arbitrary display message during a call. Send text goes out in an INFORMATION message. Defaults to name. |
Display Receive | Send /receive ISDN display IE option. The display option are a comma separated list of the following option: Block: Do not pass display text data. Name_initial: Use display text in SETUP/CONNECT messages as the party name. Name_update: Use display text in other messages NOTIFY/FACLITY for CLOP name update. Name: Combined name_initial and name_update options. Text: Pass any unused display text data as an arbitrary display message during a call. Send text goes out in an INFORMATION message. Defaults to name. |
Overlap Dialing | Enable overlap dialing mode--sending overlap digits. |
Allow Progress When Call Released | Allow inband audio (progress) when a call is RELEASEd by the far end of a PRI. |
Out-of-Band Indications | PRI Out of band indications. Enable this to report Busy and Congestion on a PRI using out-of-band notification. Inband indication, as used by the gateway doesn't seem to work with all telcos. |
Facility-based ISDN Supplementary Services | To enables transmission of facility-based ISDN supplementary services (such as caller name from CPE over facility). Cannot be changed on a reload. |
Exclusive Channel Selection | If you need to override the existing channels selection routine and force all PRI channels to be marked as exclusively selected, set this to yes. priexclusive cannot be changed on a reload. |
Ignore Remote Hold Indications | If you wish to ignores remote hold indications enable this option. |
Block Outbound Caller ID Name | Enable if you need to hide the name and not the number for legacy PPBX use. Only applies to PRI channels. |
Wait for Caller ID Name | Support Caller ID on call waiting. |
SS7
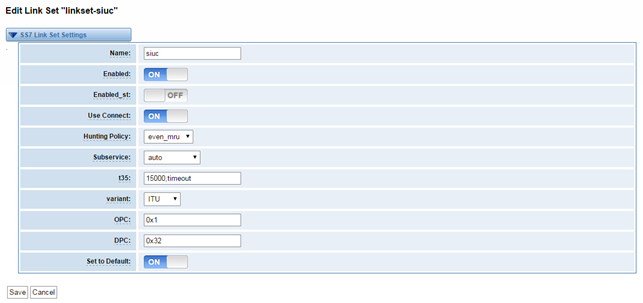
Link Set Settings
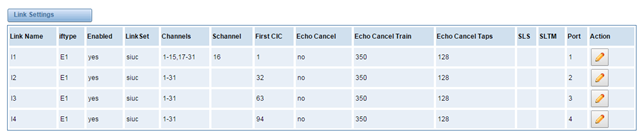
Figure 3-3-1 Link Set Settings
You can click button as shown below, when there are several link set, only one can be set to the default.
Figure 3-3-2 SS7 Link Set Settings
Table 3-3-1 Definition of SS7 Link Set Settings
Options | Definition |
Name | The linkset’s name |
Enabled | The linkset is enable or disable |
Enabled_ st | The end_of_pulsing (ST) is not used to determine when incoming address is complete |
Use Connect | Reply incoming call with CON rather than ACM and ANM |
Hunting Policy | The CIC hunting policy (even_mu, odd_lru, seq_lth, seq_htl) is even CIC numbers, most recently used |
Subservice | The subservice field: national (8), international l(0), auto or decimal/hex value; The auto means that the subservice is obtained from first received SLTM. |
t35 | The value and action for t35. Value is in msec, action is either st or timeout; if you use overlapped dialing dial plan, you might choose:t35=>4000,st |
variant | Running under SS7 standard |
OPC | The point code for this SS7 signaling point |
DPC | The destination point (peer) code |
Set to Default | Set the linkset as the default linke set |
Link Settings
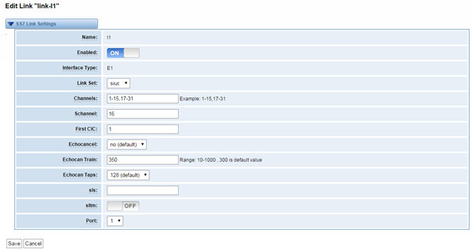
Figure 3-3-3 Link Settings
You can click button as shown below.
Figure 3-3-4 SS7 Link Settings
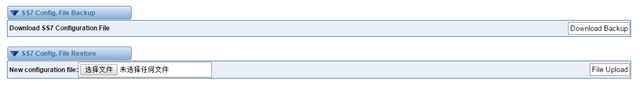
SS7 Config. File Backup and Restore
Figure 3-3-5 Config. File Backup and Restore
MFC/R2
Advanced: Interface Type
Figure 3-4-1 Advanced: Interface Type
Table 3-4-1 Definition of Interface Type
Options | Definition |
RX Gain | Gain for the rx channel. Default:0.0 |
TX Gain | Gain for the tx channel. Default:0.0 |
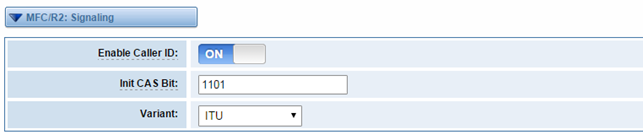
MFC/R2: Signaling
Figure 3-4-2 MFC/R2: Signaling
Table 3-4-2Definition of MFC/R2: Signaling
Options | Definition |
Enable Caller ID | Whether or not to use caller ID |
Init CAS Bit | The initial position of the CAS bits. |
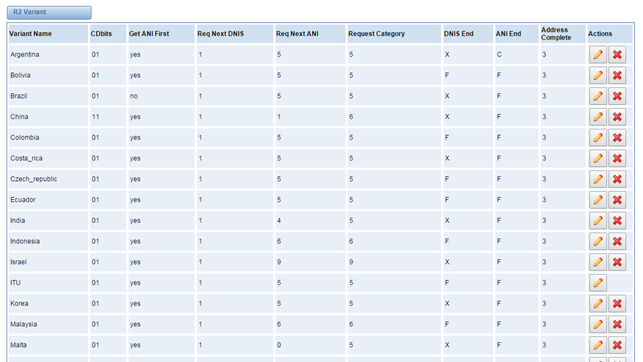
Figure 3-4-3 R2 Variant
you can click button, then you could fine the below.
Modify R2 Variant
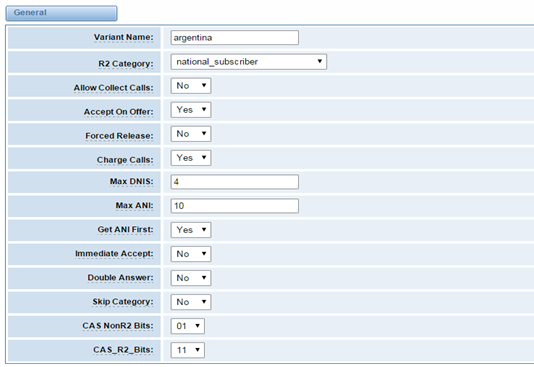
Figure 3-4-4 General
Table 3-4-3 Definition of General
Options | Definition | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Variant Name |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
R2 Category | Usually national_subscriber works just fine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Allow Collect Calls | Default is to block collect calls | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Accept On Offer | With this set to ‘no’ then the call will NOT be accepted on offered, and the call will start irs execution in extensions. Conf until the channel is answered. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Forced Release | Brazil use a special signal to force the release of the line instead of the normal clear back signal | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Charge Calls | Whether or not report to the other end ‘accept call with charge’, when interconnecting with old PBXs this may be useful | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Max DNIS | Max amount of DNIS to ask for | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Max ANI | Max amount of ANI to ask for | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Get ANI First | Whether or not get the ANI before getting DNIS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Immediate Accept | This feature allows to skip the use of Group B/II signals and go directly to the accepted state for incoming calls | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Double Answer | This will cause that every answer signal is changed by answer->clear back->answer, sort of flash | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Skip Category | Skip request of calling party category and ANI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CAS NonR2 Bits | Which bits are never used | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CAS_R2_Bits | Which bits will be used |
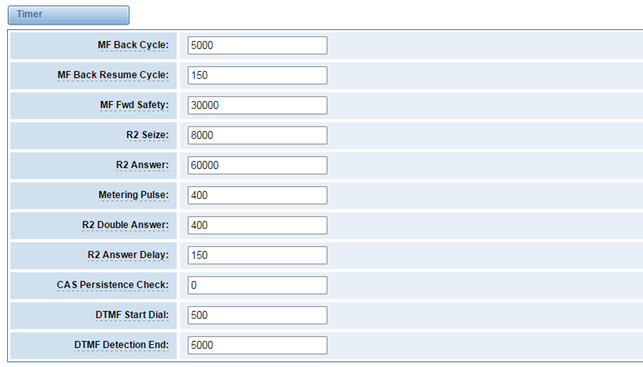
Figure 3-4-5 Timer
Table 3-4-4 Definition of Timer
Options | Definition |
MF Back Cycle | Max amount of time our backward MF signal can last |
MF Back Resume Cycle | Amount of time we set MF signal ON to resume the MF cycle with a MF pulse |
MF Fwd Safety | Safety FORWARD timer |
R2 Seize | How much time do we wait for a response to our seize signal |
R2 Answer | How much to wait for an answer once the call has been accepted |
Metering Pulse | Hoe much to wait for metering pulse detection |
R2 Double Answer | Interval between ANSWER-CLEAR BACK-ANSWER when double answer is in effect |
R2 Answer Delay | Minimum delay time between the Accept tone signal and the R2 answer signal |
CAS Persistence Check | Time to wait for to CAS signaling before handing the new signal |
DTMF Start Dial | Safety time before starting to dial DTMF |
DTMF Detection End | Safety time to decide when to stop detecting DTMF DNIS. |
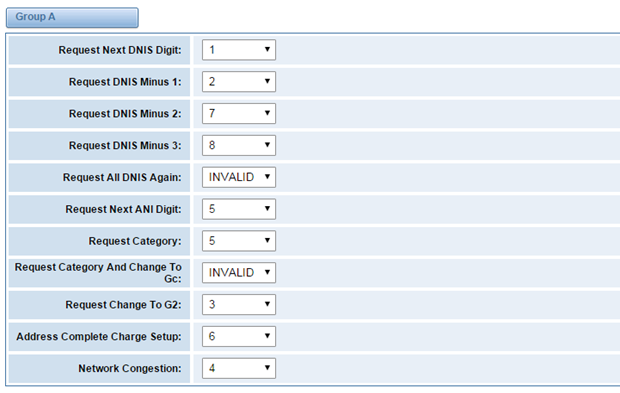
Figure 3-4-6 Group A
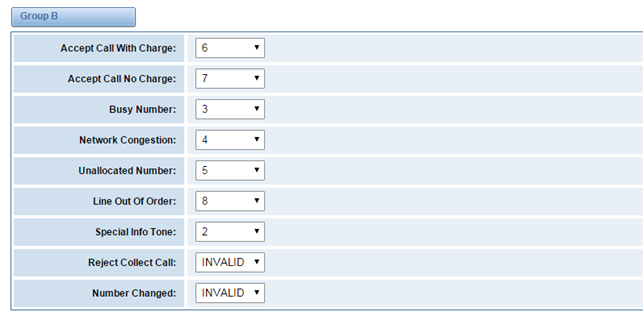
Figure 3-4-7 Group B
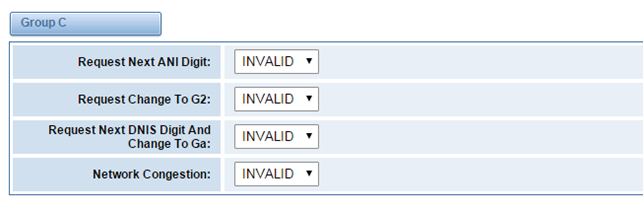
Figure 3-5-8 Group C
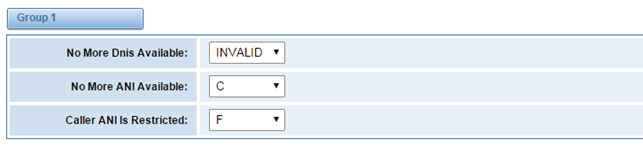
Figure 3-4-9 Group 1
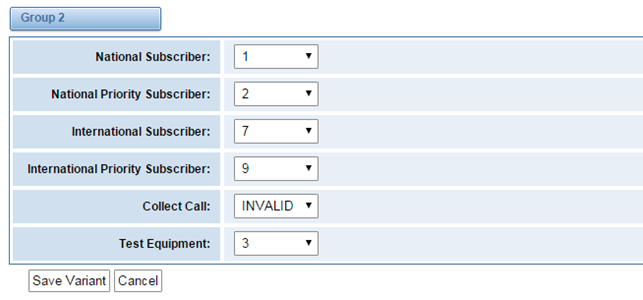
Figure 3-4-810Group 2
4.VOIP
VOIP Endpoints
SIP Endpoints
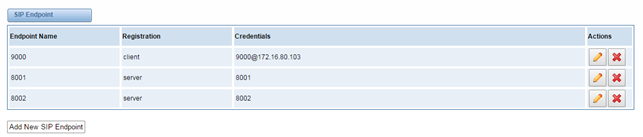
This page shows everything about your SIP, you can see status of each SIP.
Figure 4-1-1 SIP Status
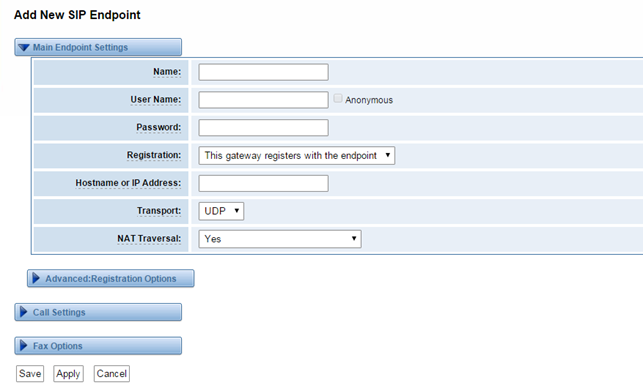
Main Endpoint Settings
You can click button to add a new SIP endpoint, and if you want to modify existed endpoints, you can click button.
There are 3 kinds of registration types for choose. You can choose Anonymous, Endpoint registers with this gateway or This gateway registers with the endpoint.
You can configure as follows:
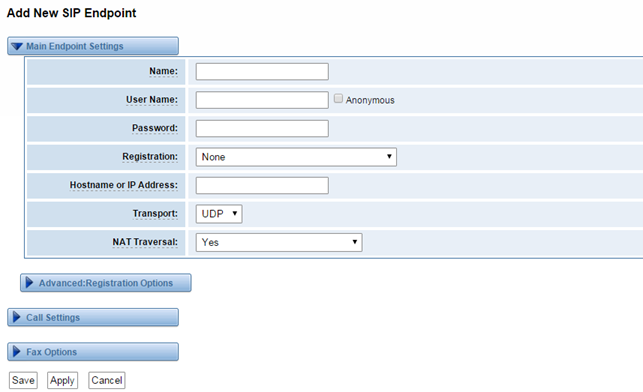
If you set up a SIP endpoint by registration “None” to a server, then you can’t register other SIP endpoints to this server. (If you add other SIP endpoints, this will cause Out-band Routes and Trunks confused.)
Figure 4-1-2 None Registration
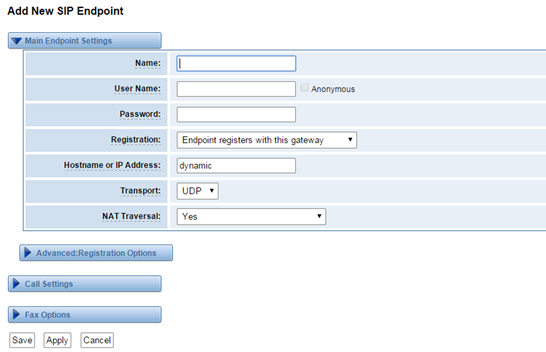
For convenience, we have designed a method that you can register your SIP endpoint to your gateway, thus your gateway just work as a server.
Figure 4-1-3 Endpoint Register with Gateway
Also you can choose registration by “This gateway registers with the endpoint”, it’s the same with “None”, except name and password.
Figure 4-1-4 This Gateway Register with the Endpoint
Table 4-1-1 Definition of SIP Options
Options | Definition |
Name | A name which is able to read by human. And it’s only used for user’s reference. |
Username | User name the end point use to authenticate with the gateway |
Password | Password the endpoint will use to authenticate with the gateway. Allowed characters |
Registration | Whether this endpoint will registers with this gateway. |
Hostname or IP Address | IP address or hostname of the endpoint or 'dynamic' if the endpoint has a dynamic IP address. This will require registration. Notice: if the input here is hostname and your DNS has changed, you must reboot asterisk. |
Transport | This sets the possible transport types for outgoing. Order of usage, when the respective transport protocols are enabled, is UDP, TCP, TLS. The first enabled transport type is only used for outbound messages until a Registration takes place. During the peer Registration the transport type may change to another supported type if the peer requests so. |
NAT Traversal | Addresses NAT-related issues in incoming SIP or media sessions. |
Advanced: Registration Options
Table 4-1-2 Definition of Registration Options
Options | Definition |
Authentication User | A username to use only for registration. |
Register Extension | When Gateway registers as a SIP user agent to a SIP proxy (provider), calls from this provider connect to this local extension. |
From User | A username to identify the gateway to this endpoint. |
From Domain | A domain to identify the gateway to this endpoint. |
Remote Secret | A password which is only used if the gateway registers to the remote side. |
Port | The port number the gateway will connect to at this endpoint. |
Qualify | Whether or not to check the endpoint's connection status. |
Qualify frequency Frequency | How often, in seconds, to check the endpoint's connection status. |
Outbound Proxy | A proxy to which the gateway will send all outbound signaling instead of sending signaling directly to endpoints. |
Call Settings
Table 4-1-3 Definition of Call Options
Options | Definition |
DTMF Mode | Set default DTMF Mode for sending DTMF. Default: rfc2833. |
Trust Remote-Party-ID | Whether or not the Remote-Party-ID header should be trusted. |
Send Remote-Party-ID | Whether or not to send the Remote-Party-ID header. |
Caller ID Presentation | Whether or not to display Caller ID. |
Advanced: Signaling Settings
Table 4-1-4Definition of Signaling Options
Options | Definition |
Progress Inband | If we should generate in-band ringing. Always use ‘never’ to never use in-band signalling, Even in cases where some buggy devices might not render it. Valid values: yes, no, never. Default: never. |
Append user=phone to URI | Whether or not to add;’ user=phone’ to URIs that contain a valid phone number. |
Add Q.850 Reason Headers | Whether or not to add Reason header and to use it if it is available. |
Honor SDP Version | By default, the gateway will honor the session version number in SDP packets and will only modify the SDP session if the version number changes. Turn This option off to force the SDP session version number and treat all SDP data as new data. This is require for devices that send non-standard SDP packets (observed with Microsoft OC S).By default This option is on. |
Allow Transfers | Whether or not to globally enable transfers. Choosing ‘no’ will disable all transfers (unless enable in peers or users). Default is enabled. |
Allow Promiscuous Redirects | Whether or not to allow 302 or REDIR to non-local SIP address .Note that promiscredir when redirects are made to the local system will cause loops since this gateway is incapable of performing a ‘hairpin’ call. |
Max Forwards | Setting for the SIP Max-Forwards header (loop prevention). |
Send TRYING on REGISTER | Send 100 Trying when the endpoint registers. |
Advanced Timer Settings
Table 4-1-5 Definition of Timer Options
Options | Definition |
Default T1 Timer | This timer is used primarily in INVITE transactions. The default for Timer T1 is 500ms or the measured run-trip time between the gateway and the device if you have qualify=yes for the device. |
Call Setup Timer | If a provisional response is not received in this amount of time, the call will auto-congest. Defaults to 64 times the default T1 timer. |
Session Timers | Session-Timers feature operates in the following three modes: originate, Request and run session-timers always; accept, run session-timers only when requested by other UA; refuse, do not run session timers in any case. |
Minimum Session | Minimum session refresh interval in seconds. Default is 90secs. |
Maximum Session Refresh Interval | Maximum session refresh interval in seconds. Defaults to 1800s. |
Session Refresher | The session refresher, uac or uas. Defaults to uas. |
Table 4-1-6 Definition of Fax Options
Options | Definition |
Mode | Working mode T.38 and T.30 |
Enabled | Enabled |
Error Correction | Error Correction |
Max Datagram | In some cases,T.38 endpoints will provide a T38FaxMxDatagram value (during T.38 setup) that is based on an incorrect interpretation of the T.38 recommendation, and result in failures because Asterisk does not believe it can send T.38 packets of a reasonable size to that endpoint (Cisco media gateway are one example of this situation).In these cases, during a T.38 call you will see warring messages on The console/in the logs from the Asterisk UDPTL stack complaining about lack of buffer space to send T.38FaxMaxDatagram value specified by the other end[point, and use a configured value instead. |
Fax Detect | FAX detection will cause the SIP channel to jump to the ‘faX’ extension (if exists) based one or more events being detected. The events that can be detected are an incoming CNG tone or an incoming T.38 re-INVITE request. |
Fax Activity | activate T38 fax gateway with ‘timeout’ seconds |
Fax Timeout | activate T38 fax gateway with ‘timeout’ seconds |
Advanced SIP Settings
Networking
Table 4-2-1 Definition of Networking Options
Options | Definition |
UDP Bind Port | Choose a port on which to listen for UDP traffic. |
Enable TCP | Enable server for incoming TCP connection (default is no). |
TCP Bind Port | Choose a port on which to listen for TCP traffic. |
TCP Authentication Timeout | The maximum number of seconds a client has to authenticate. If the client does not authenticate before this timeout expires, the client will be disconnected.(default value is: 30 seconds). |
TCP Authentication Limit | The maximum number of unauthenticated sessions that will be |
Enable Hostname Lookup | Enable DNS SRV lookups on outbound calls Note: the gateway only uses the first host in SRV records Disabling DNS SRV lookups disables the ability to place SIP calls based on domain names to some other SIP users on the Internet specifying a port in a SIP peer definition or when dialing outbound calls with suppress SRV lookups for that peer or call. |
Enable Internal SIP Call | Whether enable the internal SIP calls or not when you select the registration option "Endpoint registers with this gateway". |
Internal SIP Call Prefix | Specify a prefix before routing the internal calls. |
NAT Settings
Table 4-2-2 Definition of NAT Settings Options
Options | Definition |
Local Network | Format:192.168.0.0/255.255.0.0 or 172.16.0.0./12. A list of IP address or IP ranges which are located inside a NA Ted network. This gateway will replace the internal IP address in SIP and SDP messages with the external IP address when a NAT exists between the gateway and other endpoints. |
Local Network List | Local IP address list that you added. |
Subscribe Network Change Event | Through the use of the test_stun_monitor module, the gateway has the ability to detect when the perceived external network address has changed. When the stun_ monitor is installed and configured, chan_sip will renew all outbound registrations when the monitor detects any sort of network change has occurred. By default this option is enabled, but only takes effect once res_stun_monitor is configured. If res_stun_monitor is enabled and you wish to not generate all outbound registrations on a network change, use the option below to disable this feature. |
Match External Address Locally | Only substitute the exeternaddr or externhost setting if it matches |
Dynamic Exclude Static | Disallow all dynamic hosts from registering as any IP address used for staticly defined hosts .This helps avoid the configuration error of allowing your users to register at the same address as a SIP provide. |
Externally Mapped TCP Port | The externally mapped TCP port, when the gateway is behind a static NAT or PAI |
External Address | The external address (and optional TCP port) of the NAT. External address=hostname [:port] specifies a static address[:port] to be used in SIP and SDP messages. Examples: External address=12.34.56.78 External address=12.34.56.78.9900
|
External Hostname | The external hostname (and optional TCP port) of the NAT. External Hostname=hostname[:port] is similar to “External address”. Examples: External Hostname=foo.dyndns.net |
Hostname Refresh Interval | How often to perform a hostname lookup. This can be useful when your NAT device lets you choose the port mapping, but the IP address is dynamic. Beware, you might suffer from service disruption when the name server resolution fails. |
RTP Settings
Table 4-2-3 Definition of RTP Settings Options
Options | Definition |
Start of RTP Port Range | Start of range of port numbers to be used for RTP. |
End of RTP port Range | End of range of port numbers to be used for RTP |
Parsing and Compatibility
Table 4-2-4 Instruction of Parsing and Compatibility
Options | Definition | ||||
| Check header tags, character conversion in URIs, and multiline headers for strict SIP compatibility(default is yes) | ||||
| Send compact SIP headers | ||||
| Allows you to change the username filed in the SDP owner string. | ||||
Disallowed SIP Methods | When a dialog is started with another SIP endpoint, the other endpoint should include an Allow header telling us what SIP methods the endpoint implements. However, some endpoint either do not include an Allow header or lie about what methods they implement. In the former case, the gateway makes the assumption that the endpoint support all known SIP methods. If you know that your SIP endpoint does not provide support for a specific method, then you may provide a list of methods that your endpoint does not implement in the disallowed_ methods option. Note that if your endpoint is truthful with its Allow header, then there is need to set this option. | ||||
Shrink Caller ID | The shrinkcallerid function removes '(', ' ', ')', non-trailing '.', and '-' not in square brackets. For example, the caller id value 555.5555 becomes 5555555 when this option is enabled. Disabling this option results in no modification of the caller id value, which is necessary when the caller id represents something that must be preserved. By default this option is on. | ||||
| Maximum allowed time of incoming registrations and subscriptions (seconds). | ||||
Minimum Registration Expiry | Minimum length of registrations/subscriptions (default 60). | ||||
| Default length of incoming/outgoing registration. | ||||
Registration Timeout | How often, in seconds, to retry registration calls. Default 20 seconds. | ||||
Number of Registration | Number of registration attempts before we give up.0=continue forever, hammering the other server until it accepts the registration. Default is 0 tries, continue forever. |
Security
Table 4-2-5 Instruction of Security
Options | Definition | |
| If available, match user entry using the 'username' field from the | |
| Realm for digest authentication. Realms MUST be globally unique according to RFC 3261. Set this to your host name or domain name. | |
| Use the domain from the SIP Domains setting as the realm. In this case, the realm will be based on the request 'to' or 'from' header and should match one of the domain. Otherwise, the configured 'realm' value will be used. | |
| When an incoming INVITE or REGISTER is to be rejected, for any reason, always reject with an identical response equivalent to valid username and invalid password/hash instead of letting the requester know whether there was a matching user or peer for their request. This reduces the ability of an attacker to scan for valid SIP usernames. This option is set to 'yes' by default. | |
Authenticate Options Requests | Enabling this option will authenticate OPTIONS requests just like INVITE requests are. By default this option is disabled. | |
Allow Guest Calling | Allow or reject guest calls (default is yes, to allow). If your gateway is connected to the Internet and you allow guest calls, you want to check which services you offer everyone out there, by enabling them in the default context. |
Media
Table 4-2-6 Instruction of Media
Options | Definition | |
| Sets type of service for SIP packets | |
| Sets type of service for RTP packets |
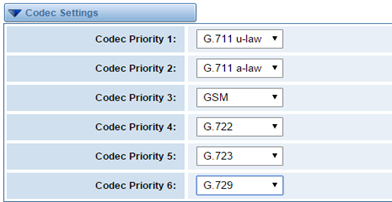
Codec Settings
Select codecs from the list below.
Figure 4-2-1 Codec Settings
Advanced IAX2 Settings
Table 4-3-1 Instruction of General
Options | Definition |
Bind Port | Bind port and bindaddr may be specified |
Bind Address | More than once to bind to multiple addresses, but the first will be the default. |
Enable IAXCompat | Cause Asterisk to spawn a separate thread when it receive a Dialplan Request instead of blocking while for a response. |
Enable No checksums | Enable No checksums. |
Enable Delay Reject | You may specify a default AMA flag for iaxtel calls. It must be one of ‘default’, ‘omit’, ‘billing’, or ‘documentation’. These flags are used in the generation of call detail records. |
ADSI | ADSI (Analog Display Services Interface) can be enable if you have (or may have) ADSI compatible CPE equipment. |
SRV Loopup | Whether or not to perform an SRV lookup on outbound calls |
AMA Flags | You may specify a global default AMA flag for iaxtel calls. These flags are used in the generation of call detail records. |
autokill | If we don’t get ACK to our NEW within 2000ms,and autokill is set to yes, then we cancel the whole thing(that’s enough time for one retransmission only ).This is used to keep things from stalling for a long time for a host that is not available for bad connections. |
Language | You may specify a global default language for users. This can be specified also on a per-user basis. If omitted, will fallback to English(en) |
Account Code | You may specify a default account for Call Detail Records (CDRs) in addition specifying on a per-user basis. |
Table 4-3-2 Instruction of Music on Hold
Options | Definition |
Mohsuggest | The ‘Mohsuggest’ option specifies which music on hold class to suggest to the peer channel when this channel place the peer on hold. It may be specified globally or on a per-user or per-peer basis. |
Mohinterpret | You may specify a global default language for users. This can be specified also on a per-user basis. If omitted, will fallback to English(en) |
Table 4-3-3 Instruction of Codec Settings
Options | Definition |
Band Width | Specify bandwith of low, medium, or high to control which codes are used in general |
Disallow | Fine tune codes here using “allow” and “disallow” clause with specific codes |
Allow | Fine tune codes here using “allow” and “disallow” clause with specific codes |
Codec Priority | Codec priority controls the codec negotiation of an inbound IAX2 call. This option is inherited to all user entity separately which will override the setting in general. |
Table 4-3-4 Instruction of Jitter Buffer
Options | Definition |
| |
Jitter Buffer | Global default as to whether you want the jitter buffer at all | ||
Force Jitter Buffer | In the ideal world, when we bridge VoIP channels we don’t want to jitter buffering on the switch, since the endpoints can each handle this. However, some endpoints may have poor jitter buffers themselves, so this option will force to always jitter buffer, even in this case. | ||
Max Jitter Buffers | A maximum size for the jitter buffer | ||
Resyncthreshold | When the jitter buffer notice a significant change in delay that continue over a few frames, it will resync, assuming that the change in delay was caused by a timestamping mix-up. The threshold for noticing a change in delay is measured as twice the measured jitter plus this resync threshold. | ||
Max Jitter Interps | The maximum number of interpolation frames the jitter buffer should return in a row. Since some clients do not send CNG/DTX frames to indicate silence, the jitter buffer will assume silence has begun after returning this many interpolations. This prevents interpolating throughout a long silence. | ||
Jitter Target Extra | Number of milliseconds by which the new jitter buffer will pad its size. The default is 40, so without modification, the new jitter buffer will set its size to the jitter value may help if your network normally has low jitter, but occasionally has spikes. | ||
Table 4-3-5 Instruction of Misc Settings
Options | Definition |
IAX Thread Count | Establishes the number of iax helper thread to handle I/O |
IAX Max Thread Count | Establishes the number of extra dynamic threads that may by spawned to handle I/O |
Max Call Number | limits the amount of call numbers allowed for each individual remote IP address. |
MaxCallNumbers_Nonvalidated | used to set the combined number of call numbers that can be allocated for connections where call token validation has been disabled. |
Table 4-3-6 Instruction of Quality of Service
Options | Definition |
Tos | Type of service |
Cos | Class of service |
Advanced Fax Settings
Table 4-4-1 Instruction of Quality of Fax Settings
Options | Definition |
UDPTL Start | DPTL start configure addresses |
UDPTL End | DPTL end configure addresses |
UDPTL Checksums | Whether to enable or disable UDP checksums on UDPTL traffic |
UDPTL FEC Entries | The number of error correction entries in a UDPTL packet |
UDPTL FEC Span | The span over which parity is calculated for FEC in a UDPTL packet |
Use Even Ports | Some VoIP providers will only accept an offer with an even-numbered UDPTL port. Set this option so that Asterisk will only attempt to use even-numbered ports when negotiating T.38. Default is no. |
Maximum Transmission Rate | Maximum Transmission Rate |
Minimum Transmission Rate | Minimum Transmission Rate |
Send Progress/Status events to manager session | Manager events with ‘call’ class permissions will receive events indicating the steps to initiate a fax session. Fax completion events are always sent to manager sessions with ‘call’ class permissions, regardless of the value of this option. |
Modem Capabilities | Set this value to modify the default modem options. Defasult:v17,v27,v29 |
ECM | Enable/disable T.30 ECM(error correction mode) by default |
5. Routing
Figure 5-1-1 Routing Rules
You are allowed to set up new routing rule by , and after setting routing rules, move rules’ order by pulling up and down, click button to edit the routing and to delete it. Finally click the button to save what you set. shows current routing rules. Otherwise you can set up unlimited routing rules.
Call Routing Rule
There is an example for Routing rules number conversion, it transform calling, called number at the same time. Suppose you want eleven numbers start at 159 to call the eleven numbers of start at 136. Calling transform delete the three numbers from left, then writing number 086 as prefix, delete the last four numbers, and then add number 0755 at the end, it will show caller name is OpenVox. Called transform adds 086 as prefix , and Change the last two number to 88.
Figure 5-1-2
processing rules | prepend | prefix | Match pattern | SdfR | StA | RdfR | Caller Name |
Calling Transformation | 086 | 159 | ×××××××× | 4 | 0755 |
| OpenVox |
Called transformation | 086 | 136 | ×××××××× | 2 | 88 |
| N/A |
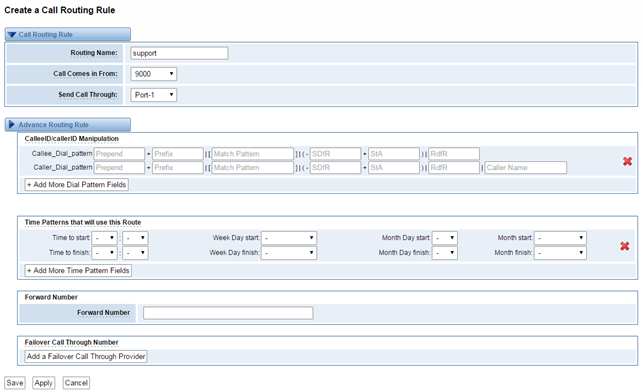
You can click button to set up your routings.
Figure 5-1-3 Example of Set Up Routing Rule
The figure above realizes that calls from “support” SIP endpoint switch you have registered will be transferred to Port-1. When “Call Comes in From” is 9000, “prepend”, “prefix” and “match pattern” in “Advanced Routing Rule” are ineffective, and just “CallerID” option is available.
Table 5-1-1 Definition of Routing Options
Options | Definition |
Routing Name | The name of this route. Should be used to describe what types of calls this route matches (for example, 'SIP2GSM' or 'GSM2SIP'). |
Call Comes in From | The launching point of incoming calls. |
Send call Through | The destination to receive the incoming calls. |
Table 5-1-2 Description of Advanced Routing Rule
Options | Definition |
Dial Patterns that will use this Route | A Dial Pattern is a unique set of digits that will select this route and send the call to the designated trunks. If a dialed pattern matches this route, no subsequent routes will be tried. If Time Groups are enabled, subsequent routes will be checked for matches outside of the designated time(s). prefix: Prefix to remove on a successful match. match pattern: The dialed number will be compared against the prefix + this match pattern. SDfR(Stripped Digits from Right): The amount of digits to be deleted from the right end of the number. If the value of this item exceeds the length of the current number, the whole number will be deleted. RDfR( Reserved Digits from Right) :Designated information to be added to the right end of the current number. StA(Suffix to Add):Designated information to be added to the right end of the current number. Caller Name: What caller name would you like to set before sending this call to the endpoint. Native language charset is allowable, e.g. Chinese charset, Latin charset. |
Forward Number | What destination number will you dial? This is very useful when you have a transfer call. |
Failover Call Through Number | The gateway will attempt to send the call out each of these in the order you specify. |
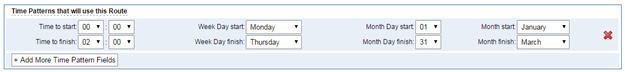
You can create various time routes and use these time conditions to limit some specific calls.
Figure 5-1-4 Advance Routing Rule
Figure 5-1-5 Time Patterns that will use this Route
If you configure like this, then from January to March, from the first day to the last day of these months, from Monday to Thursday, from 00:00 to 02:00, during this time (meet all above time conditions), all calls will follow this route. And the time will synchronize with your Sever time.
Figure 5-1-6 Change Rules
You can configure forward number when you have a transfer call.
Figure 5-1-7 Failover Call Through Number
You can add one or more “Failover Call Through Numbers”.
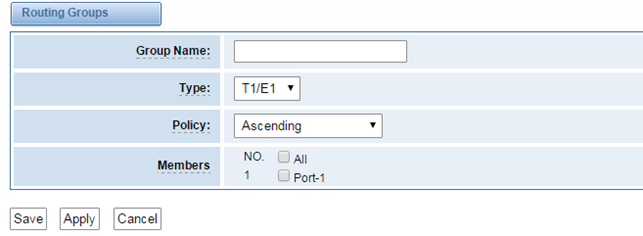
Groups
Sometimes you want to make a call through one port, but you don’t know if it is available, so you have to check which port is free. That would be troublesome. But with our product, you don’t need to worry about it. You can combine many Ports or SIP to groups. Then if you want to make a call, it will find available port automatically.
Figure 5-2-1 Establish Group
6. Network
- On “Network” page, there are three sub-pages, “WAN Settings”, “DDNS Settings”, “Toolkit” .
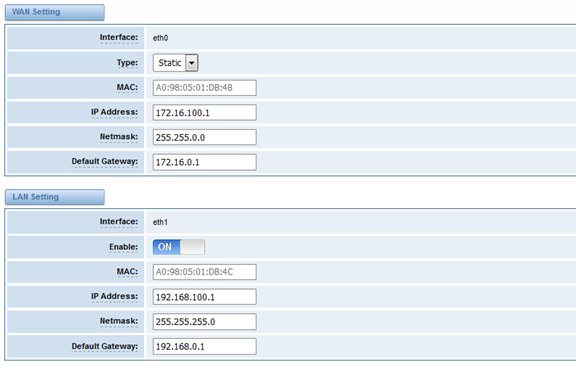
WAN/LAN Settings
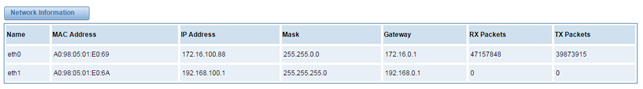
There are two types of WAN port IP, Static and DHCP. Static is the default type, and it is 172.16.100.1. The LAN port is a fixed IP and it is 192.168.100.1.
Figure 6-1-1 WAN/LAN Settings Interface
Table 6-1-1Definition of WAN/LAN Settings
Options | Definition | |
Interface | Specify which interface to capture packets from. ‘All’ means capture packets from all interfaces. |
|
Type | The method to get IP. Static: manually set up your gateway IP. DHCP: automatically get IP from your local LAN. |
|
MAC | Physical address of your network interface. |
|
Address | The IP address of your gateway. |
|
Network | The subnet mask of your gateway. |
|
Default Gateway | Default getaway IP address. |
|
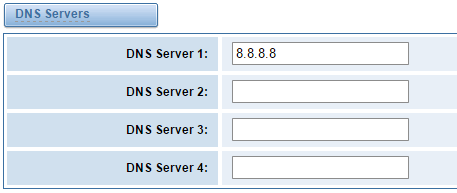
Basically this info is from your local network service provider, and you can fill in four DNS servers.
Figure 6-1-2 DNS Interface
DNS Servers: A list of DNS IP address. Basically this info is from your local network service provider.
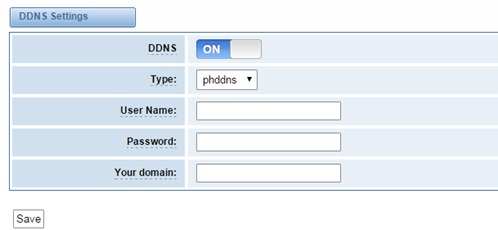
DDNS Settings
You can enable or disable DDNS (dynamic domain name server).
Figure 6-2-1 DDNS Interface
Table 6-2-1 Definition of DDNS Settings
Options | Definition | |
DDNS | Enable/Disable DDNS(dynamic domain name server) |
|
Type | Set the type of DDNS server. |
|
Username | Your DDNS account’s login name. |
|
Password | Your DDNS account’s password. |
|
Your domain | The domain to which your web server will belong. |
|
Toolkit
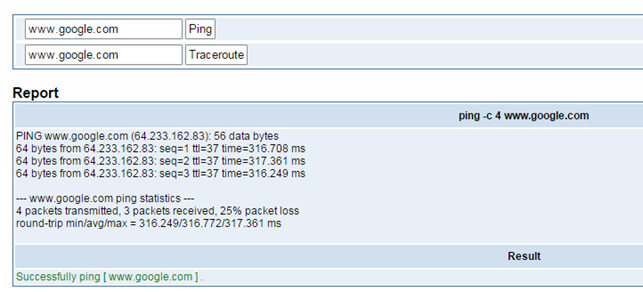
It is used to check network connectivity. Support Ping command on web GUI.
Figure 6-3-1 Network Connectivity Checking
7. Advanced
Asterisk API
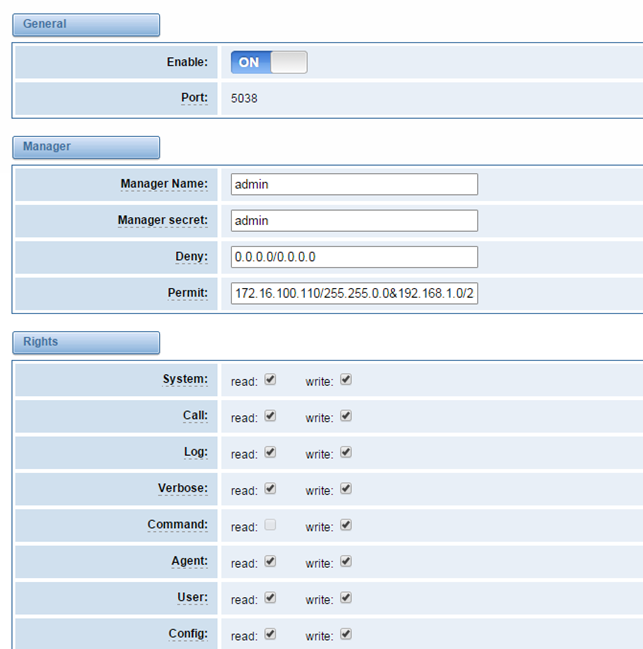
When you make “Enable” switch to “ON”, this page is available.
Figure 7-1-1 API Interface
Table 7-1-1 Definition of Asterisk API
Options | Definition | |
Port | Network port number |
|
Manager Name | Name of the manager without space |
|
Manager secret | Password for the manager. Characters: Allowed characters “-_+.<>&0-9a-zA-Z”. Length:4-32 characters. |
|
Deny | If you want to deny many hosts or networks, use char & as separator. Example: 0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0 or 192.168.1.0/255.255.255.0&10.0.0.0/255.0.0.0 |
|
Permit | If you want to permit many hosts or network, use char & as separator. Example: 0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0 or 192.168.1.0/255.255.255.0&10.0.0.0/255.0.0.0 |
|
System | General information about the system and ability to run system management commands, such as Shutdown, Restart, and Reload. |
|
Call | Information about channels and ability to set information in a running channel. |
|
Log | Logging information. Read-only. (Defined but not yet used.) |
|
Verbose | Verbose information. Read-only. (Defined but not yet used.) |
|
Command | Permission to run CLI commands. Write-only. |
|
Agent | Information about queues and agents and ability to add queue members to a queue. |
|
User | Permission to send and receive UserEvent. |
|
Config | Ability to read and write configuration files. |
|
DTMF | Receive DTMF events. Read-only. |
|
Reporting | Ability to get information about the system. |
|
Dialplan | Receive NewExten and Var Set events. Read-only. |
|
Originate | Permission to originate new calls. Write-only. |
|
All | Select all or deselect all. |
|
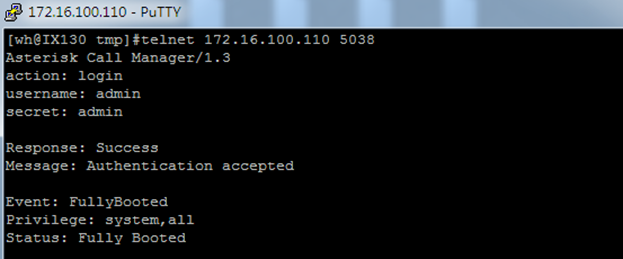
Once you set like the above figure, the host 172.16.100.110/255.255.0.0 is allowed to access the gateway API. Please refer to the following figure to access the gateway API by putty. 172.16.100.110 is the gateway’s IP, and 5038 is its API port.
Figure 7-1-2 Putty Access
Asterisk CLI
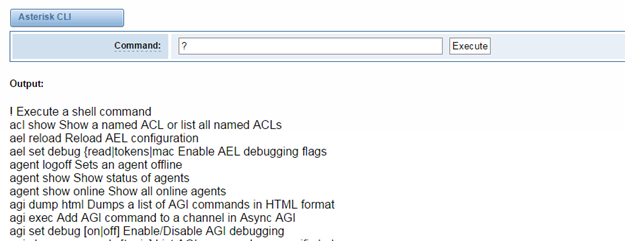
In this page, you are allowed to run Asterisk commands.
Figure 7-2-1 Asterisk Command Interface
Table 7-2-1 Definition of Asterisk CLI
Options | Definition |
Command | Type your Asterisk CLI commands here to check or debug your gateway. e.g, type “help” or “?” you will get all help information. |
If you type “help” or “?” and execute it, the page will show you the executable commands.
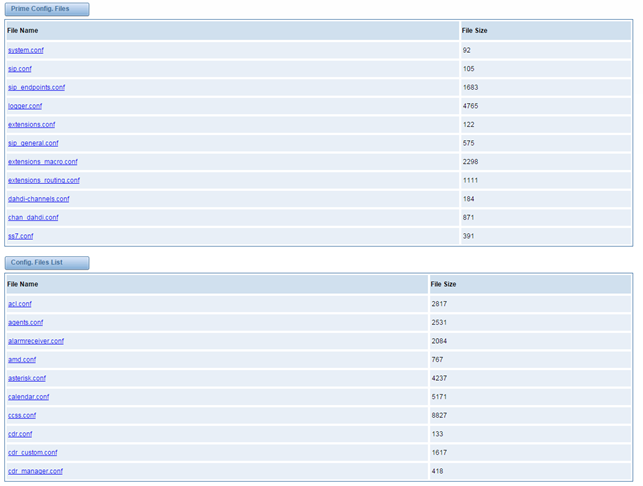
Asterisk File Editor
On this page, you are allowed to edit and create configuration files.
Click the file to edit.
Figure 7-3-1 Configuration Files List
Click “New Configuration File” to create a new configuration file. After editing or creating, please reload Asterisk.
8. Logs
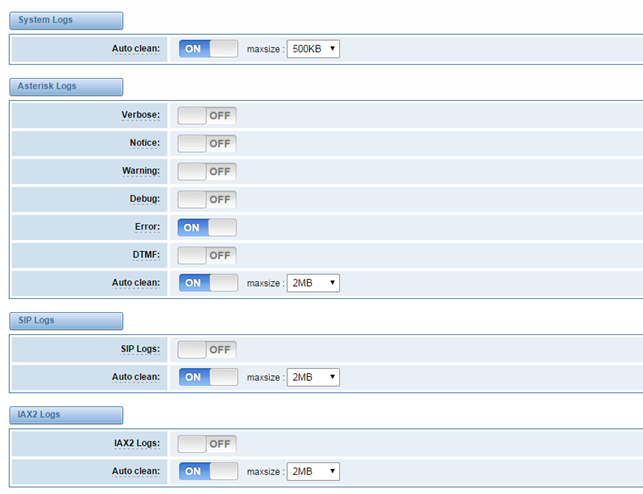
On the “Log Settings” page, you should set the related logs on to scan the responding logs page. For example, set “System Logs” on like the following, then you can turn to “System” page for system logs, otherwise, system logs is unavailable. And the same with other log pages.
Log Settings
Figure 8-1-1 Logs Settings
Table 8-1-1 Definition of Logs
Options | Definition |
Auto clean: (System Logs) | switch on : when the size of log file reaches the max size, the system will cut a half of the file. New logs will be retained. switch off : logs will remain, and the file size will increase gradually. default on, default size=1MB |
Verbose: | Asterisk console verbose message switch. |
Notice: | Asterisk console notice message switch. |
Warning: | Asterisk console warning message switch. |
Debug: | Asterisk console debug message switch. |
Error: | Asterisk console error message switch. |
DTMF: | Asterisk console DTMF info switch. |
Auto clean: (asterisk logs) | switch on : when the size of log file reaches the max size, the system will cut a half of the file. New logs will be retained. Switch off: logs will remain, and the file size will increase gradually. default on, default size=100KB |
SIP Logs: | Whether enable or disable SIP log. |
Auto clean: (SIP logs) | switch on : when the size of log file reaches the max size, the system will cut a half of the file. New logs will be retained. Switch off: logs will remain, and the file size will increase gradually. default on, default size=2MB |
IAX2 Logs | Whether enable or disable IAX log |
Auto clean | switch on : when the size of log file reaches the max size, the system will cut a half of the file. New logs will be retained. Switch off: logs will remain, and the file size will increase gradually. default on, default size=2MB |
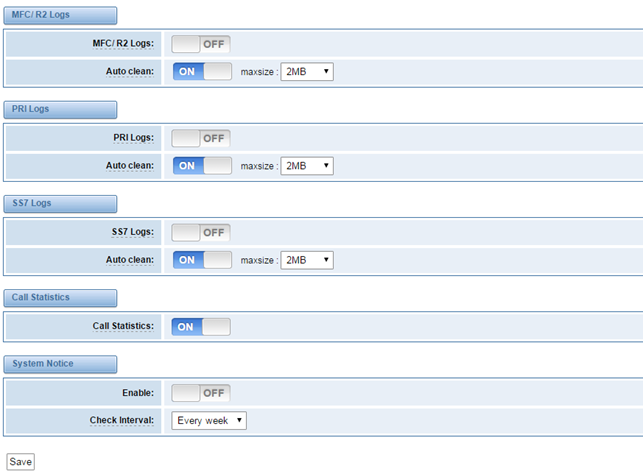
MFC/ R2 Logs | Whether enable or disable MFC/ R2 Logs log. |
Auto clean | switch on : when the size of log file reaches the max size, the system will cut a half of the file. New logs will be retained. Switch off: logs will remain, and the file size will increase gradually. default on, default size=100KB |
PRI Logs | PRI port logs. You can choose one or more ports. If you choose "All", the "PRI" page will show you the logs about all the ports. |
Auto clean (PRI logs) | switch on : when the size of log file reaches the max size, the system will cut a half of the file. New logs will be retained. Switch off: logs will remain, and the file size will increase gradually. default on, default size=2MB |
.SS7 Logs | Whether enable or disable SS7 log |
Auto clean | switch on : when the size of log file reaches the max size, the system will cut a half of the file. New logs will be retained. Switch off: logs will remain, and the file size will increase gradually. default on, default size=100KB |
Call Statistics | Whether enable or disable Call Statistics. |
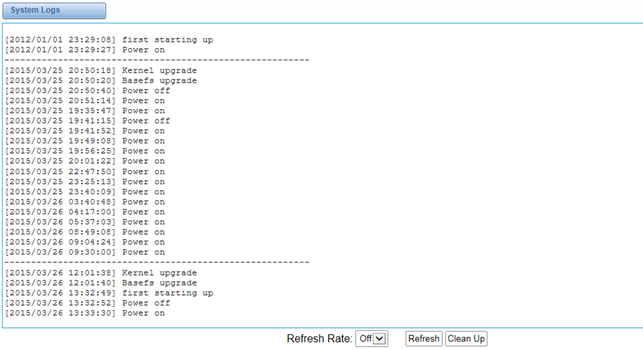
System
Figure 8-2-1System Logs Output
Asterisk
Figure 8-3-1 Asterisk Logs
On the pages of “system”, ”Asterisk”, “SIP”, “IAX2”, “SS7”, and “MFC/R2”, there are some functions: Displays the log by port, refresh regularly and log download.
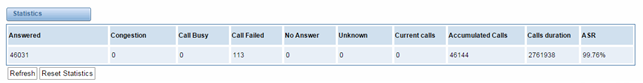
Statistics
Figure 8-9-1 Call Statistics
The figure of call statistics, you’ll find “Answered” “Congestion” “Call Busy” “Call Failed” “No Answer” “Current Calls” “Unknown” “Current calls” “Accumulated Calls” “Calls duration” and “ASR”.