

OpenVox VoxStack Series GSM Gateway is an open source asterisk-based GSM VoIP Gateway solution for SMBs and SOHOs. With friendly GUI and unique modular design, users may easily setup their customized Gateway. Also secondary development can be completed through AMI (Asterisk Management Interface).
There are two models with VoxStack series GSM Gateway VS-GW1202-8G and VS-GW1600. There are 4/8 GSM channels in VS-GW1202-8G. The Modular Design GSM Gateways are ranging from 4 up to 20 GSM channels on the VS-GW-1600 series gateways, developed for interconnecting the GSM cellular networks with a wide selection of codecs and signaling protocol, including G.711A, G.711U, G.729, G.722, G.723, G.726 and GSM to quickly reduce communication expenses and maximize cost-savings. With the unique design of the VoxStack gateway, it can support hot-swap for both SIM cards and GSM gateway modules. Users can simply add or remove the modules for hardware expansion or exchange.
TheVoxStack gateway designs with 2 LAN switch boards to provide stack ability on the hardware upgrade, and five VS-GWM400G modules which are independent with each other, so each one has a GUI configuration web. If you connect to ETH1, you can access Board 1 only and access other boards with different port numbers which can avoid IP conflict. Otherwise if you connect to ETH2, you can access different Boards with different IP addresses.
Our products support SMS messages sending, receiving, group sending and SMS to E-mail. The GSM gateway will be 100% compatible with Asterisk, Elastix, trixbox, 3CX, FreeSWITCH SIP server and VOS VoIP operating platform.

Figure 1-1 TopologicalGraph

Figure 1-2 Product Appearance

Figure 1-3 Front Panel
Network Data Switch Board: ETH1, ETH2.
VoxStack provides 2 working modes: Stand-alone and Cluster.
Table 1-1 ETH2 IP Addresses
| Stack Num | IP | Username | Password |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 172.16.99.1 | admin | admin |
| 2 | 172.16.99.2 | admin | admin |
| 3 | 172.16.99.3 | admin | admin |
| 4 | 172.16.99.4 | admin | admin |
| 5 | 172.16.99.5 | admin | admin |
Default IP: 172.16.99.1

Figure 1-4 Front Panel

Figure 1-5 LED Indicator
Default IP: 172.16.99.1
Username: admin
Password: admin
Every VS-GWM400G is independent with each other, please enter the default IP in your browser to scan and configure the module you want. For the first time, please enter every IP to configure every module one by one. Now we offer you two ways to access to your gateway. There are two RJ45 Network ports on the board, ETH1 and ETH2. They are different. If chooseETH1, you can access Board 1 only, then access to other boards with different port numbers but the same IP address, this will helpto avoid IP conflict. If you choose ETH2, you can access different Boards with different IP addresses.
Notice: Log in

Figure 1-6 LOG Interface
On the “Status” page, you will find all GSM, SIP, Routing, Network information and status.

Figure 2-1 System Status
Table 2-1 Description of System Status:
| Options | Definition |
|---|---|
| Port | Number of GSM ports. |
| Signal | Display the signal strength of in each channels of GSM. |
| BER | Bit Error Rate. |
| Carrier | Display the network carrier of current SIM card. |
Registration Status | Indicates the registration status of current GSM module. |
| PDD | Post Dial Delay (PDD) is experienced by the originating customer as the time from the sending of the final dialed digit to the point at which they hear ring tone or other in-band information.Where the originating network is required to play an announcement before completing the call then this definition of PDD excludes the duration of such announcements. |
| ACD | The Average Call Duration (ACD) is calculated by taking the sum of billable seconds (bill sec) of answered calls and dividing it by the number of these answered calls. |
| ASR | Answer Seizure Ratio is a measure of network quality. Its calculated by taking the number of successfully answered calls and dividing by the total number of calls attempted. Since busy signals and other rejections by the called number count as call failures, the ASR value can vary depending on user behavior. GSM Status Show the status of port, include blank space and “READY”. Black space means it is unavailable here and “Ready” means the port is available |
| Remain Time | This value is multiplied by to step length is a rest call time. |
Table 2-2 Description of Time Settings:
| Options | Definition |
|---|---|
| System Time | Your gateway system time |
| Time Zone | The world time zone. Please select the one which is the same or the closest as your city |
| POSIX TZ String | Posix time zone strings. |
| NTP Server 1 | Time server domain or hostname. For example, [time.asia.apple.com]. |
| NTP Server 2 | The first reserved NTP server. For example, [time.windows.com]. |
| NTP Server 3 | The second reserved NTP server. For example, [time.nist.gov]. |
| Auto-Sync from NTP | Whether enable automatically synchronize from NTP server or not. ON is enable, OFF is disable this function. |
| Sync from NTP | Sync time from NTP server. |
| Sync from Client | Sync time from local machine. |
For example, you can configure like this:

Figure 2-2 Time Settings
You can set your gateway time Sync from NTP or Sync from Client by pressing different buttons.
Your gateway doesn't have administration role. All you can do here is to reset what new username and password to manage your gateway. And it has all privileges to operate your gateway. You can modify “Web Login Settings” and “SSH Login Settings”. If you have changed these settings, you don’t need to log out, just rewriting your new user name and password will be OK. Also you can specify the web server port number.
Table 2-3 Description of Login Settings:
| Options | Definition |
|---|---|
| User Name | Define your username and password to manage your gateway, without space here. Allowed characters "-_+. < >&0-9a-zA-Z". Length: 1-32 characters. |
| Password | Allowed characters "-_+. < >&0-9a-zA-Z". Length: 4-32 characters. |
| Confirm Password | Please input the same password as 'Password' above. |
| Port | Specify the web server port number. |

Figure 2-3 Login Settings
Notice: Whenever you do some changes, do not forget to save your configuration.
You can choose different languages for your system. If you want to change language, you can switch “Advanced” on, then “Download” your current language package. After that, you can modify the package with the language you need. Then upload your modified packages, “Choose File” and “Add”.

Figure 2-4 Language Settings
If switch it on, you can manage your gateway to reboot automatically as you like. There are four reboot types for you to choose, “By Day, By Week, By Month and By Running Time”.

Figure 2-5 Reboot Types
If use your system frequently, you can set this enable, it can helps system work more efficient.
OpenVox GSM Gateway offers you two ways to cluster your gateway: Automatic Cluster or Manual Cluster. When you first time log in your gateway, you will only see 4 ports of one module. Then you can press  button, the system will search other modules in the LAN and communicate.
button, the system will search other modules in the LAN and communicate.

Figure 2-6 Automatic Cluster
If you want to choose Manual Cluster, you should switch Detail on first.
There are five VS-GWM400G modules which are independent with each other integrated in one GSM Gateway, so we offer 3 kinds of Working Modes.

Figure 2-7 Working Modes
Notice: You can choose Remain Original IP address ON or OFF. If set it on, you can log in your getaway with Original IP and Target IP.
table 2-4 Definition of Master Options:
| Options | Definition |
|---|---|
Mode | Stand-alone Mode Master Mode Slave Mode |
Password (master mode) | Master Mode password. Must be 4~16 bits digital 0-9 |
Master IP(Local IP) (master mode) | Master’s target IP. Must be set in the subnet different from external subnet, so that the external subnet couldn’t access internal subnet |
| Slaves IP List | Set the slaves’s original and target IP. The original IP is outward IP, and the target IP is inward IP. Up to four slaves. |
On the “Tools” pages, there are reboot, update, upload, backup and reset toolkits.
You can choose system reboot and asterisk reboot separately.

Figure 2-8 Reboot Tools
If you press "OK", your system will reboot and all current calls will be dropped. Asterisk Reboot is the same.
Instrution of reboots:
We offer 2 kinds of update types for you, you can choose System Update or System Online Update. System Online Update is an easier way to update your system, if you choose it, you will see some information below.

Figure 2-9 Update Firmware
If you want to update your system and remain your previous configuration, you can first backup configuration, then you can upload configuration directly. That will be very convenient for you.

Figure 2-10 Upload and Backup Configuration
Sometimes there is something wrong with your gateway that you don’t know how to solve it, mostly you will select factory reset. Then you just need to press a button, your gateway will be reset to the factory status.

Figure 2-11 Restore Configuration
On the “Information” page, there shows some basic information about the T1/E1 gateway. You can see software and hardware version, storage usage, memory usage and some help information.

Figure 2-12 Information
You can see much information about your SIM cards on this page.

Figure 3-1 GSM Settings
On this page, you can see your GSM module status and click action  button to configure the port.
button to configure the port.

Figure 3-2 Port Configuration
As you see, we have offered “Band” option, you can select different bands easily and you have many options.

Figure 3-3 Band Binding
If you have set your Pin Code, you can check on like this:

Figure 3-4 PIN Code Application
Then input your password, system will identify numbers of SIM cards. It can help to prevent SIM card from being stolen and improve security.
If you want to hide your number when you call out, you can just switch CLIR “ON” (Of course you need your operator’s support).

Figure 3-5 CLIR Application
If you have some voice quality problems, you can open Echo Cancellation for an attempt.

Figure 3-6 Echo Cancellation
One more feature, we offer you IMEI automatically modification

Figure 3-7 Automatically IMEI Modify
We have offered you IMEI modification function. If you want to modify your IMEI number, please do as follows. You can log in your gateway and modify IP address as follows. Input web site below on your
browser. http://172.16.99.1/cgi-bin/php/gsm-autoimei.php. Then you will see the following picture. Don’t forget to switch “Enable” to “ON”, or you can’t change your IMEI numbers.

Figure 3-8 IMEI Modification
Also you can choose to modify one or more certain ports or all ports. You can set automatic modification interval by filling in the time you want. 
If you choose “Immediately”, then the ports you have chosen will modify IMEI numbers at once. On the contray, system will keep time from now until the time of next modification. And If you choose “Force”, System will hang up all your current calls, then modify IMEI.
You can press to do some settings. We offer you two ways to modify your IMEI. You can choose Autogeneration or Manual.
to do some settings. We offer you two ways to modify your IMEI. You can choose Autogeneration or Manual.

Figure 3-9 Advanced Settings
As you can see, you can set any number you wan for every port. “X” means any digits from 0 to 9.
You just need to fill in “Set to All ”, then press “Set to All”, you can see the interface as above. Don’t forget to press “Save”. Then “Current IMEI” will change. That means Autogeneration. If you want to set a certain number as your IMEI, you can press “Manual”. Then you will be required to input a new IMEI.

Figure 3-10 Manual
After configuration, you can press “Back Home” to return your gateway interface.
table 3-1 Definition of GSM Settings:
| Options | Definition |
|---|---|
| Name | The alias of the GSM port. Input name without space here. Allowed characters "-_+.<>&0-9a-zA-Z".Length: 1-32 characters. |
| Speaker Volume | The speaker volume level, the range is 0-100. This will adjust the loud speaker volume level by an AT command. |
| Microphone Volume | The microphone volume, range is: 0-15. This will change the microphone gain level by an AT command. |
| DAC Gain | The range is: -42 to +20 |
| ADC Gain | The range is: -42 to +20 |
| Dial Prefix | The prefix number of outgoing calls from this GSM channel |
| PIN Code | Personal identification numbers of SIM card. PIN code can be modified to prevent SIM card from being stolen. |
| Custom AT commads when start | User custom AT commands when start system, use “|” to split AT command. |
| CLIR | Caller ID restriction, this function is used to hidden caller ID of SIM card number. The gateway will add ‘#31#’ in front of mobile number. This function must support by Operator. |
| SMS Center Number | Your SMS center number of your local carrier. |
| GSM Module IMEI | You can click “Modify” button and automatically modify it. |
Now we can offer you two types of call duration limit, you can choose “Single Call Duration Limit” or “Call Duration Limitation” to control your calling time
First you need to switch “Enable” on, then you can set “Step” and “Single Call Duration Limitation” any digits you want. When you make a call by this port, it will limit your calling time within the product of
Step * Single Call Duration Limitation
And if your calling time overtops the value above, the system will hang up this call.

Figure 3-11 Single Settings

Figure 3-12 Call Duration Limitation Settings
The same algorithm with single time limitation, the total calling time of this port can’t beyond the product of “Step” and “Call Duration Limitation”.
If the duration of a call is less than “Minimum Charging Time”, it will be not included in “Call Duration”.
You can set a digit for “Alarm Threshold”, when the call minutes less than this value, the gateway will send alarm info to designated phone.
You can enable your Auto Reset, then choose by day, by week, or by month.

Figure 3-13 Auto Reset Settings
You can save your configuration to other ports.

Figure 3-14 Save To Other Ports
If you have set like this, you will see many  on the Web GUI, you can set whether to check.
on the Web GUI, you can set whether to check.
Notice: When you do some changes, you need to Save and Apply, then “Remain Time” will show as you set.
Your calling status will show on the main interface.

Figure 3-15 GSM Information
Description of Call Duration Limit Settings
Sometimes it’s not convenient for you to answer a call, if you don’t want to lose some important calls, you can choose Call Forwarding. You can choose Call Forwarding Unconditional, Call Forwarding No Reply, Call Forwarding Busy or Call Forwarding on Not Reachable. If want to cancel your call forwarding settings, you can choose Cancel All.

Figure 3-16 Call Forwarding
Notice: Don’t forget to save your settings. Please first press button, then press button..
You can do some DTMF Detection Settings if you choose “GSM -> DTMF”.

Figure 3-17 DTMF Detection Settings
Notice: If you don’t have special need, you don’t have to modify these settings. You can just choose “Default”.
You can get USSD information, send AT command and check number with this module. When you have a debug of the GSM module, AT command is useful.

Figure 3-18 Function Options
Definition of Functions
If you want to send AT command, first you should input your command, then select certain ports and choose “Copy to Selected”, finally choose “Execute”.

Figure 3-19 AT Command Example
This page shows everything about your SIP, you can see status of each SIP.

Figure 4-1 SIP Endpoints
You can click  button to add a new SIP endpoint, and if you want to modify existed endpoints, you can click
button to add a new SIP endpoint, and if you want to modify existed endpoints, you can click  button.
button.
There are 3 kinds of registration types for choose. You can choose Anonymous, Endpoint registers with this gateway or This gateway registers with the endpoint.
You can configure as follows:
If you set up a SIP endpoint by registration “None” to a server, then you can’t register other SIP endpoints to this server. (If you add other SIP endpoints, this will cause Out-band Routes and Trunks confused.)

Figure 4-2 None Registration
For convenience, we have designed a method that you can register your SIP endpoint to your gateway, thus your gateway just work as a server.

Figure 4-3 Endpoint Register With this Gateway
Also you can choose registration by “This gateway registers with the endpoint”, it’s the same with “None”, except name and password.

Figure 4-4 This Gateway Register With the Endpoint
table 4-1 Definition of SIP Options
| Options | Definition |
|---|---|
| Name | Display name |
| Username | Register name in your SIP server |
| Password | Authenticating with the gateway and characters are allowed. |
| Registration | None --- Not registering; Endpoint registers with this gateway --- When register as this type, it means the GSM gateway acts as a SIP server, and SIP endpoints register to the gateway; This gateway registers with the endpoint --- When register as this type, it means the GSM gateway acts as a client, and the endpoint should be register to a SIP server; |
| Hostname or IP Address | IP address or hostname of the endpoint or 'dynamic' if the endpoint has a dynamic IP address. This will require registration. |
| Transport | This sets the possible transport types for outgoing. Order of usage, when the respective transport protocols are enabled, is UDP, TCP, TLS. The first enabled transport type is only used for outbound messages until a Registration takes place. During the peer Registration, the transport type may change to another supported type if the peer requests so. |
| NAT Traversal | No --- Use Rport if the remote side says to use it. Force Rport on --- Force Rport to always be on. Yes --- Force Rport to always be on and perform comedia RTP handling. Rport if requested and comedia --- Use Rport if the remote side says to use it and perform comedia RTP handling. |
Definition of Registration Options
Definition of Signaling Options
Definition of Call Options
Definition of Timer Options
Definition of Networking Options
Definition of NAT Settings Options
Definition of RTP Settings Options
Instruction of Parsing and Compatibility
Instruction of Security
Instruction of Media
Select codecs from the list below.

Figure 4-5 Codec Settings

Figure 5-1 Routing Rules
You are allowed to set up new routing rule by , and after setting routing rules, move rules’ order by pulling
, and after setting routing rules, move rules’ order by pulling  up and down, click
up and down, click  button to edit the routing and
button to edit the routing and  to delete it. Finally click the
to delete it. Finally click the  button to save what you set.
button to save what you set.  shows current routing rules. Otherwise you can set up unlimited routing rules.
shows current routing rules. Otherwise you can set up unlimited routing rules.
You can click  button to set up your routings.
button to set up your routings.

Figure 5-2 Example of Set up Routing Rule
The figure above realizes that calls from “1001” SIP endpoint switch you have registered will be transferred to Port-1. When “Call Comes in From” is T1/E1 Port, “prepend”, “prefix” and “match pattern” in “Advanced Routing Rule” are ineffective, and just “CallerID” option is available.
Definition of Routing Options
Description of Advanced Routing Rule
You can create various time routes and use these time conditions to limit some specific calls.

Figure 5-3 Time Patterns that will use this Route
If you configure like this, then from January to March, from the first day to the last day of these months, from Monday to Thursday, from 00:00 to 02:00, during this time (meet all above time conditions), all calls will follow this route. And the time will synchronize with your Sever time.

Figure 5-4 Change Rules
You can set your caller ID name and caller number as you like before sending the call to the endpoint. You can also configure forward number when you have a transfer call.

Figure 5-5 Failover Call Through Number
You can add one or more “Failover Call Through Numbers”.
Sometimes you want to make a call through one port, but you don’t know if it is available, so you have to check which port is free. That would be troublesome. But with our product, you don’t need to worry about it. You can combine many GSM or SIP to groups. Then if you want to make a call, it will find available port automatically.

Figure 5-6 Routing Group
Mobile Number Portability allows switching between mobile phone operators without changing the mobile number. Sounds simple, but there are loads of tasks performed behind the scene at the operator end.
The URL is shown in the password string way. So please type the url in other place such a txt file, check it, then copy it to the gateway. The outgoing number in the url should be replaced by the variables ${num}.
Here is an example of the MNP url:
https://s1.bichara.com.br:8181/chkporta.php?user=832700&pwd=sdsfdg&tn=8388166902
The 8388166902 is the outgoing phone number, when config the MNP url, should replce it with ${num}. Then it turns to https://s1.bichara.com.br:8181/chkporta.php?user=832700&pwd=sdsfdg&tn=${num}.

Figure 5-7 MNP Settings
You can choose enable SMS Received, SMS Local Strored and SMS Status Report or not. But if you want to see your SMS outbox, you should switch SMS Status Report ON.

Figure 6-1 SMS Settings
You can change sender options here, include resend, times of resend.

Figure 6-2 Sender Options
Description of Sender Options
This is a tool that makes it available for you to email account to transmit the SMS to other email boxes. The following settings realize that received SMS through openvpnvoip@gmail.com transmit to openvpnvoip@yahoo.com.cn, openvpnvoip@hotmail.com and support@openvox.cn

Figure 6-3 SMS to Email
Types of E-mail Box
| E-mail Box Type | SMTP Server | SMTP Port | SMTP Security Connectivity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gmail | smtp.gmail.com | 587 | √ |
| HotMail | smtp.live.com | 587 | √ |
| Yahoo! | smtp.mail.yahoo.co.in | 587 | × |
| smtp.163.com | 25 | × |
Definition of SMS to E-mail
| Options | Definition |
|---|---|
| Enable | When you choose on, the following options are available, otherwise, unavailable. |
| Email Address of Sender | To set the email address of an available email account. For example, openvpnvoip@gmail.com. |
| Domain | To set outgoing mail server. e.g. smtp.gmail.com |
| SMTP Port | To set port number of outgoing mail server. (Default is 25) |
| SMTP User Name | The login name of your existing email account. This option might be different from your email address. Some email client doesn't need the email postfix |
| SMTP Password | The password to login your existing email. |
| TLS Enable | When you choose Yahoo and 163 free e-mails, this option is not available. |
| SMTP Server | To set outgoing mail server. e.g. mail.openvox.cn. |
| Destination Email Address1 | The first email address to receive the inbox message. |
| Destination Email Address2 | The second email address to receive the inbox message. |
| Destination Email Address3 | The third email address to receive the inbox message. |
Allowing endpoints to send some specific KEY WORDS and corresponding PASSWORD to operate the gateway and message is case-sensitive. In default, this function is disabled.

Figure 6-4 SMS Control
For example, SMS control password is 123456789 which has nothing to do with the login password, you can send “get info 123456789” to the GSM module’s phone number to get your gateway’s IP information.
Definition of SMS Control
| Enable | ON(enable), OFF(disable) |
|---|---|
| Password | The password to confirm that SMS makes the gateway rebooted, shut down, restored configuration files and get info on this gateway. |
| SMS Format | For example, the message formats: reboot system PASSWORD: To reboot your whole gateway. The PASSWORD is referring to the PASSWORD you set up from option “PASSWORD” above. Reboot asterisk PASSWORD: To restart your gateway core. Restore configs PASSWORD: To reset the configuration files back to the default factory settings. Get info PASSWORD: To get your gateway IP address |
| SMS inbox Auto clean | switch on: When the size of the SMS inbox record file reaches the max size, the system will cut a half of the file. New record will be retained. switch off: SMS record will remain, and the file size will increase gradually. default on, max size = 20 MB |
You can choose one or more ports to send SMS to the destination number, different numbers should be separated by symbols: '\r', '\n', space character, semicolon and comma. Then you can see much feedback information.

Figure 6-5 SMS Sender
On this page, you are allowed to scan, delete, clean up, and export each port’s received SMS. Also you are allowed to check messages by port, phone number, time order and message keywords.

Figure 6-6 SMS Inbox

Figure 6-7 SMS Outbox

Figure 6-8 SMS Forwarding
SMS forwarding function is used to transfer the incoming sms to a destination number, such as mobile user. You can click "New Routing" button to create a new routing.
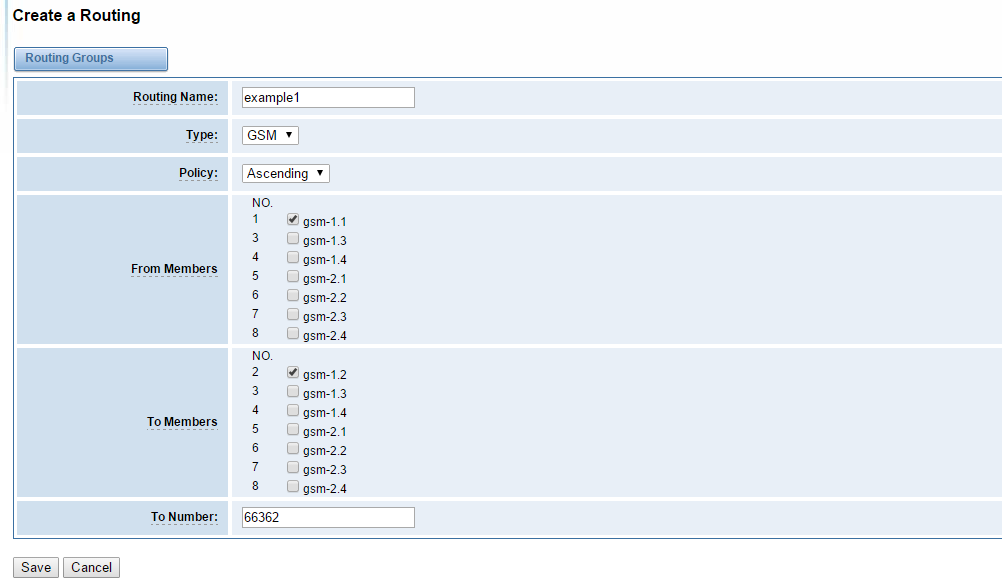
Figure 6-9 example 1 of sms forwarding routing
example 1 means that sms coming from gsm-1.1 will transfer via gsm-1.2 to phone number 66362.
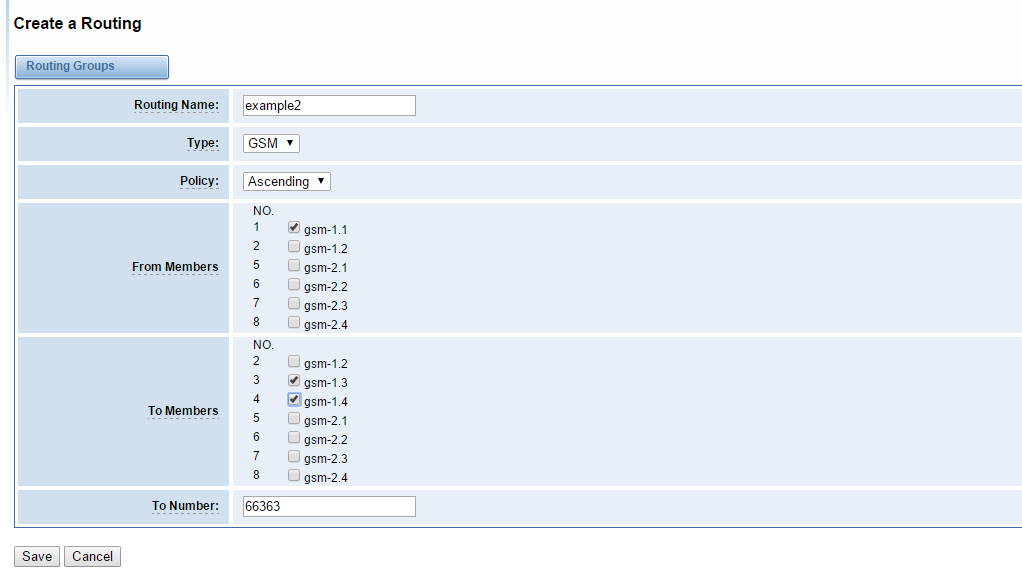
Figure 6-10 example 2 of sms forwarding routing
example2 means that sms coming from gsm-1.1 will be transfered via either gsm-1.3 or gsm-1.4 to number 66363. It will choose gsm-1.3 first. if gsm-1.3 is busy, it will use gsm-1.4.
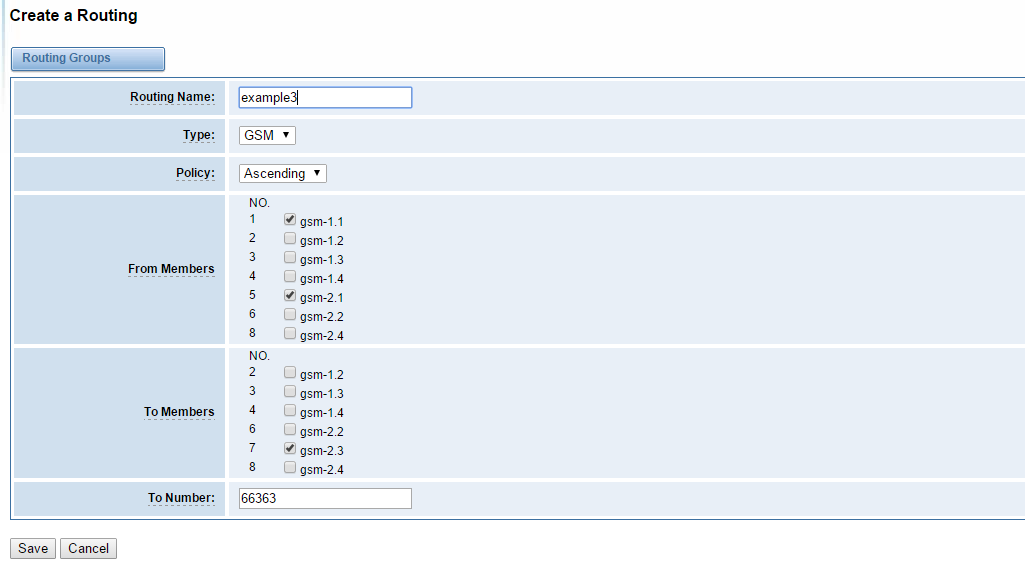
Figure 6-11 example 3 of sms forwarding routing
example3 means that sms coming from both gsm-1.1 and gsm-2.1 will be transfered via gsm-2.3 to number 66363.
On “Network” page, there are three sub-pages: “LAN Settings”, “DDNS Settings”, and “Toolkit”.
There are three types of WAN/LAN port IP, Factory, Static and DHCP. Factory is the default type, and it is 172.16.99.1. When you Choose LAN IPv4 type is “Factory”, this page is not editable.
A reserved IP address to access in case your gateway IP is not available. Remember to set a similar network segment with the following address of your local PC.

Figure 7-1 LAN Settings
Definition of LAN Settings
Basically this info is from your local network service provider, and you can fill in four DNS servers.

Figure 7-2 DNS Servers
You can enable or disable DDNS (dynamic domain name server).

Figure 7-3 DDNS Settings
Definition of DDNS Settings
It is used to check network connectivity. Support Ping command on web GUI.

Figure 7-4 Toolkit
When you make “Enable” switch to “ON”, this page is available.

Figure 8-1 Asterisk API Interface
Definition of Asterisk API
Once you set like the above figure, the host 172.16.100.110/255.255.0.0 is allowed to access the gateway API. Please refer to the following figure to access the gateway API by putty. 172.16.100.110 is the gateway’s IP, and 5038 is its API port.
Figure 8-2 Putty Access Gateway API
In this page, you are allowed to run Asterisk commands.

Figure 8-3 Asterisk CLI
Command: Type your Asterisk CLI commands here to check or debug your gateway.
Notice: If you type “help” or “?” and execute it, the page will show you the executable commands.
On this page, you are allowed to edit and create configuration files. Click the file to edit.

Figure 8-4 Asterisk File Editor
Click “New Configuration File” to create a new configuration file. After editing or creating, please reload Asterisk.
On the “Log Settings” page, you should set the related logs on to scan the responding logs page. For example, set “System Logs” on like the following, then you can turn to “System” page for system logs, otherwise, system logs is unavailable. And the same with other log pages.

Figure 9-1 Log Settings

Figure 9-2 System Logs
You can choose one specific board to see it related logs.

Figure 9-3 Choose One Board
You can scan your CDR easily on web GUI, and also you can delete, clean up or export your CDR information.

Figure 9-4 CDR Output
Recently we have made our LOGS display richer, you can see your GSM Outbound of every port clearly.

Figure 9-5 Time Patterns that will use this Route
Definition of Logs
General Info
GSM
SIP Features
Routing and Number Conversion
Business Control
System Features
Network Features
Operation Maintenance
