...
Table 1-3-1 Description of Front Panel
Interface | Function | Color | Work Status |
1 Port 1-Port4 | E1/T1 ports. The port numbers are different on different models, from 1 to 4. | ||
2 Reset | Reset button is used to restore the device. | ||
3 RUN | Register indicator | Green | Slow blinking(Green 2s and Flash 0.1s):Work normally |
Fast blinking(Green 0.5s and Flash 0.5s): Work abnormally | |||
Fast blinking(Green 0.5s and Flash 0.5s): Work abnormally | |||
No blinking: Dahdi Error | |||
4 PWR | Power Status indicator | Green | On: Power is on |
Off: Power is off | |||
5 VGA | VGA monitor connector | ||
6 Eth1 | Network interface | ||
7 Eth0 | Network interface | ||
8 USB | USB interface | ||
...
The OpenVox DGW-100X series gateways provides one or two power supply, one power named DGW-100X ,the other is named DGW-100XR, ‘R’ stands for Reduntant.
Main Features
- Based on Asterisk
R- ®
- Editable Asterisk
R- ® configuration file
- Wide selection of codecs and signaling protocol
- Support
unlimited - 512 routing rules and flexible routing settings
- Stable performance, flexible dialing, friendly GUI
- Codecs support: G.711A, G.711U, G.729, G.723, G.722, GSM
- Support ports group management
- Support call status information
- Support T.38/Pass-through fax
- Support Auto Provision, SNMP V1/V2c/V3 and TR069
- Echo Cancellation
- Connect legacy PBX systems to low-cost VoIP services
- Connect legacy PBX systems to remote sites over private VoIP links
- Connect IP PBX systems to legacy TDM services
Physical Information
Table 1-5-1 Description of Physical Information
Weight |
2842 g | |
Size | 44cm* |
23cm*4. |
3cm | |
Temperature | - |
40~85°C (Storage) |
0~70°C (Operation) |
Operation humidity |
5%~95% non-condensing |
Max power |
20 W | |
LAN port | 1 |
WAN port | 1 |
Software
Default IP: 172.16.100.1
...
Figure 1-6-1 LOG IN Interface
2. System
Status
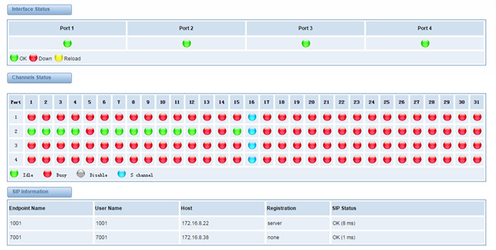
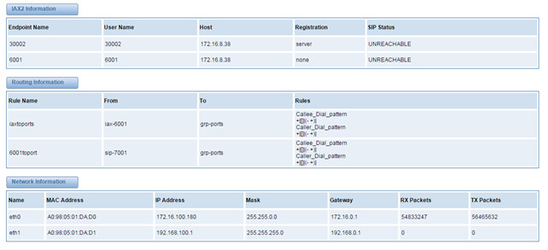
On the “Status” “System Status” page, you will find all Interface status, Channelschannels status, SIP, IAX2, Routing rules, and Network information and status.
Figure 2-1-1 System Status
...
Options | Definition |
Interface Status | Show the status of port, include "OK" and ”Down”. "Down" means no trunk line connected; "OK" means the trunk line of port is available. |
ChannelsStatus | Show the Channels status of port, include "Idle". "Busy". "Disable" and “S channel”. "Idle" means it is available; "Busy" means the channel is busy; "Disable" means it is unavailable; “S channel” means signaling channel. |
Time
Table 2-2-1Description of Time Settings
...
Options
...
Definition
...
System Time
...
Your gateway system time.
...
Call Status
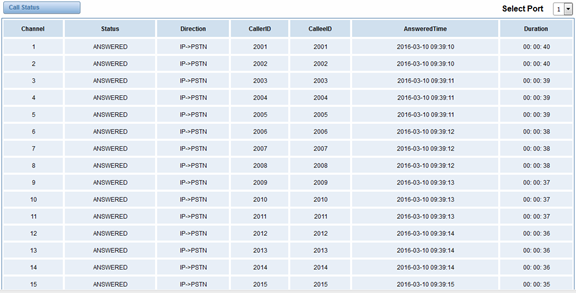
The verbose of the system call status will be present on the “Call Status” page. You can select the specified T1/E1 port which you are care for.
Figure 2-2-1 Verbose of call status
Time
Table 2-2-1Description of Time Settings
Options | Definition |
System Time | Your gateway system time. |
Time Zone | The world time zone. Please select the one which is the same or the closest as your city. |
POSIX TZ String | Posix timezone strings. |
NTP Server 1 | Time server domain or hostname. For example, [time.asia.apple.com]. |
NTP Server 2 | The first reserved NTP server. For example, [time.windows.com]. |
NTP Server 3 | The second reserved NTP server. For example, [time.nist.gov]. |
Auto-Sync from NTP | Whether enable automatically synchronize from NTP server or not. ON is enable, OFF is disable this function. |
Sync from NTP | Sync time from NTP server. |
Sync from Client | Sync time from local machine. |
...
Your gateway doesn't have administration role. All you can do here is to reset what new username and password to manage your gateway. And it has all privileges to operate your gateway. You can modify “Web Login Settings” and “SSH Login Settings”. If you have changed these settings, you don’t need to log out, just rewriting your new user name and password will be OK. Also you can specify the web server port number.Usually the web login default mode is “http and https”. For safety, you can switch to “only https” mode.
...
Table 2-3-1Description of Login Settings
Options | Definition |
User Name | Your gateway |
...
does not have administration role. All you can do here is defining the user name and password to manage your gateway. And it has all privileges to operate your gateway .User Name: Allowed characters “-_+<>&0-9a-zA-Z”.Length:1-32 characters. | |
Password | Allowed characters "-_+. <>&0-9a-zA-Z". Length: 4-32 characters. |
Confirm Password | Please input the same password as 'Password' above. |
Login Mode | Specify the web login mode: http and https, only https. Default is http and https. |
Port | Specify the web server port number. |
...
Do not use port 443 which is reserved for HTTPS. |
Figure 2-3-1 Login Settings
...
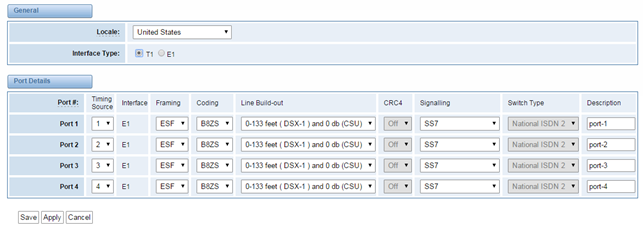
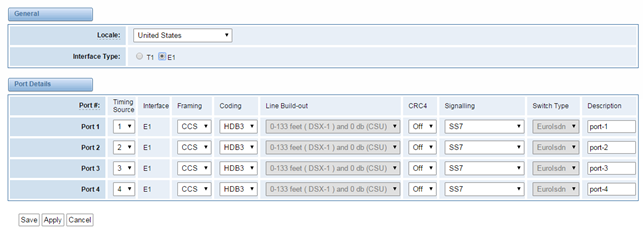
Local | Your local. This will be used for the tone style. Used when in-call indications need to be generated such as ring back, busy, congestion, and other call-oriented inband tone signals. |
Interface Type | It shows you the current type of port. It has two type:E1 and T1 |
Table 3-1-2 Definition of advanced interface type
Options | Definition |
Echo Cancellation | Whether or not to enable echo cancellation |
RX Gain
| Gain for the RX (receive -into Asterisk)channel.Default:0.0 |
TX Gain
| Gain for the TX (transmit -out of Asterisk Asterisk)channel.Default:0.0 |
Figure 3-1-2 Port 2Port Details
...
Table 3-1-3 Definition of Port Details
...
Options | Definition |
Udptl Start | DPTL start configure addresses |
Udptl End | DPTL end configure addresses |
Udptl Checksums | Whether to enable or disable UDP checksums on UDPTL traffic |
Udptl Fec Entries | The number of error correction entries in a UDPTL packet |
Udptl Fec Span | The span over which parity is calculated for FEC in a UDPTL packet |
Use Even Ports | Some VoIP providers will only accept an offer with an even-numbered UDPTL port. Set this option so that Asterisk will only attempt to use even-numbered ports when negotiating T.38. Default is no. |
Maximum Transmission Rate | Maximum Transmission Rate |
Minimum Transmission Rate | Minimum Transmission Rate |
Send Progress/Status events to manager session | Manager events with ‘call’ class permissions will receive events indicating the steps to initiate a fax session. Fax completion events are always sent to manager sessions with ‘call’ class permissions, regardless of the value of this option. |
Modem Capabilities | Set this value to modify the default modem options. Defasult:v17,v27,v29 |
ECM | Enable/disable T.30 ECM(error correction mode) by default |
5. Routing
...
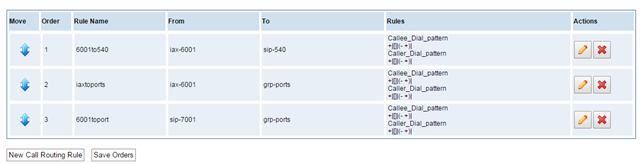
The gateway embraces the flexible and friendly routing settings for user. It supports up to 512 routing rules and about 100 pairs of calleeID/callerID manipulations can be set in a rule. It support DID function (The usage of DID function: How to use DID function with OpenVox T1/E1 Gateway). The gateway support trunk group and trunk priority management.
Figure 5-1-1 Routing Rules
...
There is an example for Routing rules number conversion, it transform calling, called number at the same time. Suppose you want eleven numbers start at 159 to call the eleven numbers of start at 136. Calling transform delete the three numbers from left, then writing number 086 as prefix, delete the last four numbers, and then add number 0755 at the end, it will show caller name is openvox China Telecom. Called transform adds 086 as prefix , and Change the last two number to 88.
...
processing rules | prepend | prefix | Match pattern | SdfR | StA | RdfR | Caller Name |
Calling Transformation | 086 | 159 | ×××××××× | 4 | 0755 | OpenVox | China Telecom |
Called transformation | 086 | 136 | ×××××××× | 2 | 88 |
| N/A |
...
Click “New Configuration File” to create a new configuration file. After editing or creating, please reload Asterisk.
...
7.
...
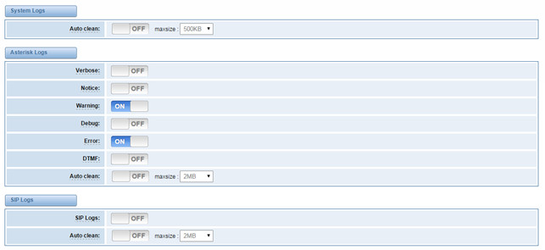
On the “Log Settings” page, you should set the related logs on to scan the responding logs page. For example, set “System Logs” on like the following, then you can turn to “System” page for system logs, otherwise, system logs is unavailable. And the same with other log pages.
Log Settings
...
4 Auto Provisioning
Auto provisioning or auto-configuration is an easy, flexible and time-saving way to upgrade firmware and configurations for E1 gateways in mass deployment. With auto provisioning, all user information can be entered via the central ACS (Auto Configuration Server). ACS can be DHCP server or TFTP, HTTP and FTP server. It will not take effects immediately but in the next time system is power on. It could be postponed the execution of restart system also.
Note that system will not be upgrade the firmware and update configurations if the connection between ACS and gateway is disconnect.
7.4.1 Preparation
The following should be prepared before anto provisioning being applied.
l Enable the auto provisioning in gateway
l The ACS has been prepared
l The network between gateway and ACS is connected
7.4.2 Configuring gateway
Usually, the feature is disabled before being on sale. To activate the auto provisioning function, please follow the procedures as below.
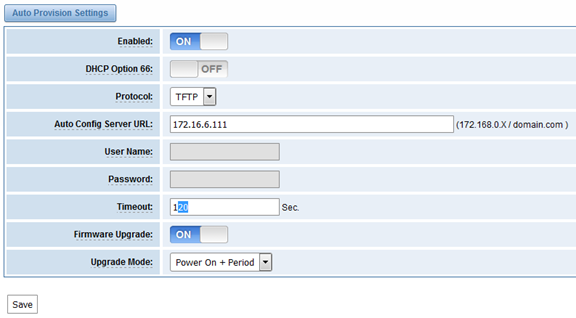
Step 1 On the ADVANCED-> Auto Provision interface
Step 2 Enable the ‘Enabled’ option and select ACS. DHCP option 66 can be enabled if ACS has been work as DHCP server, otherwise please select protocol of provisioning and fill the value of ‘Auto Config Server URL’. Username and password may need to be filled in FTP/HTTP for the purpose of system safety. Do not forget to select Firmware upgrade, upgrade mode and fill the value of timeout, and click ‘Save’.
Step 3 Set interval of checking in LOGS->System notice then enable it, and click ‘Save’.
Table 7-4-1 Definition of Auto Provision
Options | Definition |
Enabled | Whether to enable or disable Auto Provision |
DHCP Option 66 | Get ACS server address from Option 66 via DHCP |
Protocol | Set protocol of connection |
Auto Config Server URL | The config server domain or IP address |
User Name | The account of downloading from ACS |
Password | The password of downloading from ACS |
Timeout | The max limit time for downloading firmware |
Firmware Upgrade | Enable/disable the mode of downloading firmware |
Upgrade Mode | Select upgrade time. Power: start upgrade configuration when Power on. Power + Period: Set the frequency of checking the latest configuration when gateway running |
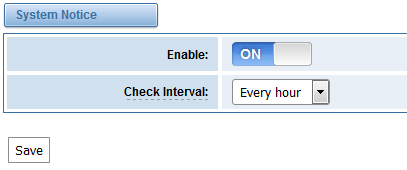
Table 7-4-2 Definition of system notice
Options | Definition |
Enable | Whether to enable or disable system notice |
Check Interval | When Upgrade Mode is set, this parameter specifies the interval of Checking. |
Figure 7-4-1 Auto Provision interface
7.4.3 Configuring ACS
The Auto Configuration Server can be the one of TFTP, FTP and HTTP server. The ACS is used to store the firmware release and configurations files of the devices under management.
List the primary files in ACS download directory as table 7-4-3:
Table 7-4-3 Definition of ACS files
Options | Definition |
DGW100x-current.bin | The firmware image |
common.conf | The wildcard configuration file for the whole gateway |
defconfig.tar.gz | The default(factory) configuration file |
EPC-{mac}.conf | The private configuration file for the specified gateway. Naming rules: “EPC-“ + “mac” +”.conf”. The naming prefix of “EPC-” stands for the private configuration file, “mac” is the physical address of network interface card but removed semicolon and “.conf” is the suffix. For example, the EPC-a0980501dbca.conf, ‘a0980501dbca’ is the MAC address (A0:98:05:01:DB:CA). |
The format of common.conf , EPC-{mac}.conf and defconfig.tar.gz:
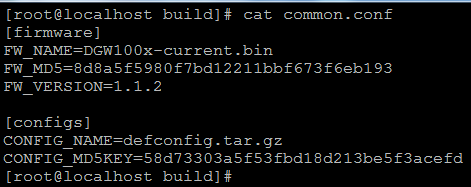
(1). Common.conf
[firmware]
FW_NAME=DGW100x-current.bin //Firmware image name
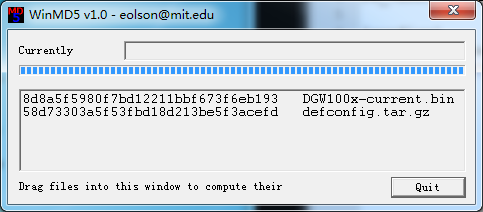
FW_MD5=b3603f3c3b5e7eb6326498640f151c79 //The md5 of firmware image
FW_VERSION=1.1.2 //Firmware version
[configs]
CONFIG_NAME=defconfig.tar.gz // default configuration file(compressed)
CONFIG_MD5KEY=2cd2dfbe52482405350816e3698cb530 // the md5 of default configuration file
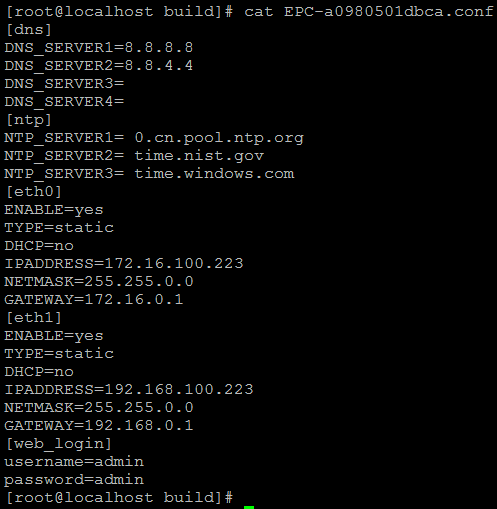
(2).EPC-{mac}.conf
[dns]
DNS_SERVER1=8.8.8.8
DNS_SERVER2=8.8.4.4
DNS_SERVER3=
DNS_SERVER4=
[ntp]
NTP_SERVER1= 0.cn.pool.ntp.org
NTP_SERVER2= time.nist.gov
NTP_SERVER3= time.windows.com
[eth0]
ENABLE=yes
TYPE=static
DHCP=no
IPADDRESS=172.16.100.223
NETMASK=255.255.0.0
GATEWAY=172.16.0.1
[eth1]
ENABLE=yes
TYPE=static
DHCP=no
IPADDRESS=192.168.100.223
NETMASK=255.255.0.0
GATEWAY=192.168.0.1
[web_login]
username=admin
password=admin
(3). Defconfig.tar.gz
Figure 7-4-2 the overview of defconfig.tar.gz
7.4.4 Provisioning example
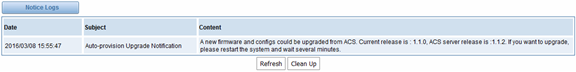
After auto provisioning is enabled, the gateway will visit the Auto Configuration Server and download the updated files periodically based on the timer Check Interval (LOGS->System notice). By default, the timer is set as every hour. System will receive a message from ACS, like figure 7-4-3, and the message will be display in the system notice (LOGS->System Notice).
Auto provisioning will not take effects immediately but in the next time system is power on. It could be postponed the execution of restart system also.
Now, an example of using Auto Provisioning will be given in the following.
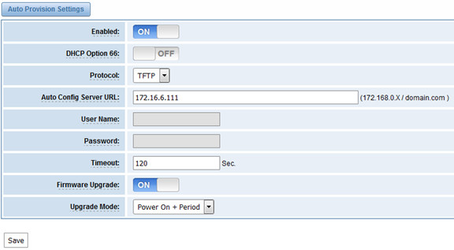
- Activate the auto provision (TFTP) in ADVANCED-> Auto Provision like figure 7-4-4.
Figure 7-4-4 Auto provision settings
- Enable the check interval in LOGS->Log settings->System Notice like figure 7-4-5.
Figure 7-4-5 Check interval setting
- Configuring the ACS(Generate the md5 of firmware and defconfig.tar.gz)
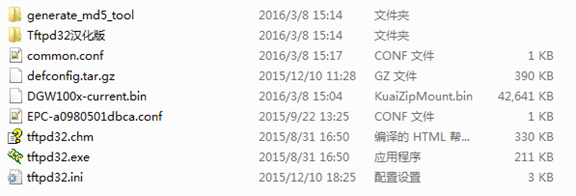
l Copy the firmware, defconfig.tar.gz, common.conf and EPC-{mac}.conf to the working directory of TFTP server.
Figure 7-4-6 The working directory of TFTP server
Notice:
The demo of E1 gateway mac address is A0:98:05:01:DB:CA (eth0), therefore the private configuration file is EPC-a0980501dbca.conf.
l Generate the md5 of firmware and defconfig.tar.gz. Then fill in common.conf and EPC-{mac}.config.
Figure 7-4-7 Generate the md5 of firmware and configuration
Figure 7-4-8 Common.conf
Figure 7-4-7 EPC- a0980501dbca.conf
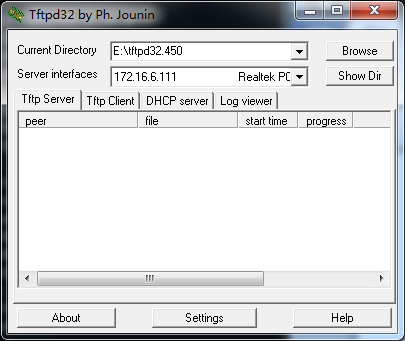
l Start TFTP service. Tftpd32.exe is a useful TFTP tools in windows7, then make sure TFTP server is select.
Figure 7-4-8 Demo TFTP server
- The system will receive an auto provision message in web GUI.
Figure 7-4-9 System notice logs
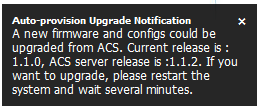
Figure 7-4-10 Auto provision upgrade notification
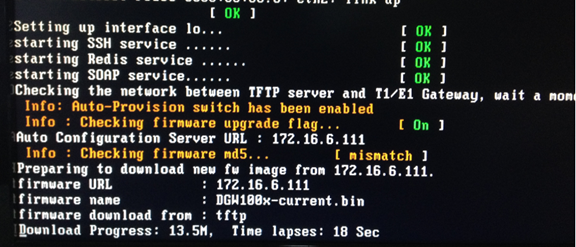
- Restart the system. It will take about 3 minutes almost to download, upgrade Firmware and update configurations.
Figure 7-4-11Downloading the firmware and configs
Figure 7-4-12Applying the firmware and configs
7.5 SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an application–layer protocol, which is used to manage and monitor network elements and exchange management information between network devices. By default SNMP uses port 161 for communication.
Since the inception SNMP, it embraces three versions: v1, v2c and v3. V1 and v2c are the most implemented version of SNMP; v3 is target at the high security when compare to its older versions. The gateway support private SNMP MIBs (private enterprise number) to access.
7.5.1 Parameters in SNMP setting
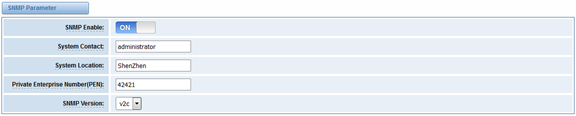
Table 7-5-1Definition of SNMP setting
Options | Definition |
SNMP Enable | Whether to enable SNMP |
System Contact | System contact information(optional) |
System Location | The locale of system contact(optional) |
Private Enterprise Number | The number is used for defining private SNMP MIBs which is assigned by Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA). For more information, please access: |
SNMP Version | Select version of SNMP |
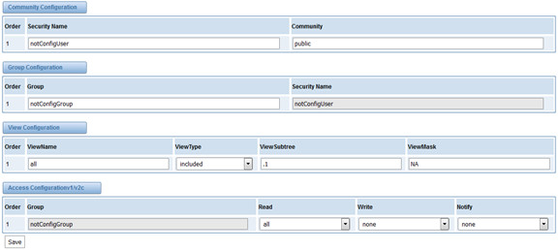
Community Configuration | Define a community name to security name |
Group Configuration | Define the security name to a group |
View Configuration | Set a view to let the group have rights to do |
Access Configuration | Grant the group can access to the view(read/write/notify) |
User Configuration | Only exist in v3. Add a v3 account to SNMP. Notice that the length of auth password and privacy password are more than 8. |
7.5.2 Activating SNMP
Usually, the feature is disabled by default. To activate the SNMP feature, please follow the Figure 7-5-1.
The Interface is in the ADVANCED->SNMP. System contact, location and private enterprise number are optional. Figure 7-5-1 is the SNMP setting interface.
Figure 7-5-1 Activating the SNMP
Note: Do not forget to click ‘Save’ to take effect. After configuration, The SNMP feature is activated immediately.
7.5.3 Verify SNMP
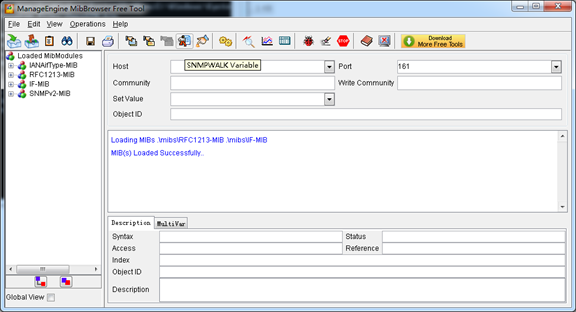
A powerful, indispensable and easy-to-use MIB browser is convenient for engineer/manager to manage SNMP enabled network devices and applications. In this session, Manage Engine MIB browser is selected. It allows user to issue SNMP requests to retrieve agent's data, or make changes to the agent. It is free tool for Windows, Mac and Linux.
(1). Get SNMP parameters via SNMP MIB browser. It’s supposed that Manage Engine MIB browser is installed perfectly. Figure 7-5-2 is the main interface of Manage Engine MIB browser.
Figure 7-5-2 Manage Engine MIB browser
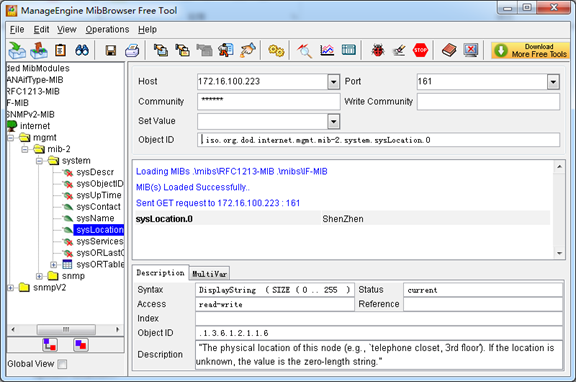
And the field of Host, Port and Community are filled with 172.16.100.223, 161 and public respectively. Object ID is the node of SNMP MIBs, e.g. “.1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0” is system location and “.1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0” is system description.
Figure 7-5-3 Get system location
After the rest field has been filled, then verify it. Click Operations->GET to get the value of system location and it returns the value which we just set.
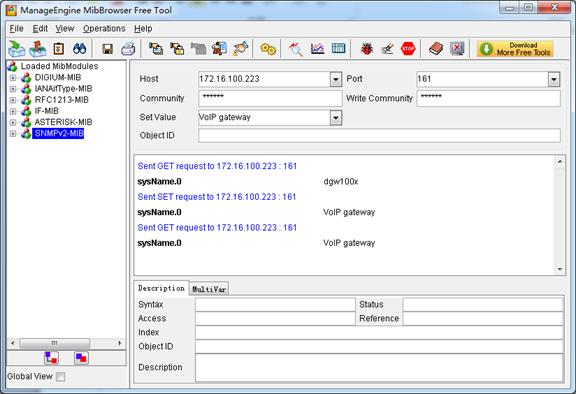
(2). Set SNMP parameters via SNMP MIB browser. For example, set the system name. system name is “dgw100x” by default, then set it as “VoIP gateway”. See figure 7-5-4.
l Click Operations->GET to attain the current system name.
l Fill the field of Set Value with “VoIP gateway”.
l Click Operations->SET to set the system name.
l Click Operations->GET to attain the modified system name.
Figure 7-5-4 Set system name
7.6 TR069
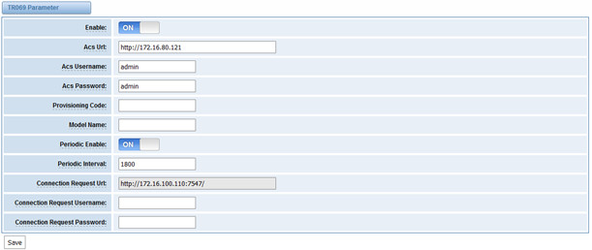
TR069 is a remote management solution which offers a single interface to manage the ACS and automate the deployment and support of data, voice and video services, thereby reducing operation and support costs, while enhancing customer satisfaction. Its user-friendly interface covers the entire service lifecycle, from centralized remote provisioning of services, to inventory management, group updates, monitoring, event triggering, and support automation. Figure 7-6-1 is TR-069 configuration interface and table 7-6-1 is its definition.
Table 7-6-1 Definition of TR069 configuration interface
Options | Definition |
Acs Url | Specify the URL of the ACS |
Acs Username | Specify the user name to be used by the device to authenticate with the ACS. |
Acs Password | Specify the password to be used by the device to authenticate with the file server |
Provisioning Code | Information of the device vendor, which may be used to indicate the primary service provider and other provisioning information to the ACS. It can be numbers or English letters. |
Model Name | A brief description of the interface type or name. It is a string of characters. |
Periodic Enable | Used to specify whether to periodically report to the ACS. |
Periodic Interval | The interval for reporting to the ACS. |
Connection Request Url | The address used for the ACS to connect back to the device. |
Connection Request Username | The account used for the ACS to connect back to the device, for example, admin. |
Connection Request Password | The password used for the network management server to connect back to the device. |
Figure 7-6-1 TR069 configuration interface
7.7 Network Capture
The gateway have been supplied a network packets capture in the web for ease of user to analysis, capture and monitor the gateway’s network status, RTP flows, protocol analysis and so on.
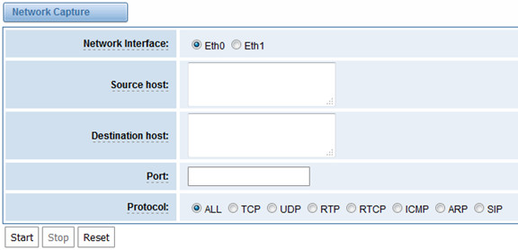
Table 7-7-1 Definition of Network capture
Options | Definition |
Network Interface | Specify which interface to be capture packets from. ‘All’ means capture packets from all interfaces |
Source host | Specify which source host IP address to listen for |
Destination host | Specify which destination host IP address to listen for |
Port | To specify a port that is either source or destination direction |
Protocol | To specify which protocol to be captured, ‘All’ stands for capture multi-protocols, the SIP default port is 5060, If you are using a different port, please amend it. |
The interface is in ADVANCED->Network Capture.
Figure 7-7-1 Network capture interface
8. Logs
On the “Log Settings” page, you should set the related logs on to scan the responding logs page. For example, set “SIP Logs” on like the following, then you can turn to “SIP” page for sip logs, otherwise, sip logs is unavailable. And the same with other log pages.
Figure 8-1-1 Logs Settings
...
Options | Definition | |||
Auto clean: (System Logs) | switch on : when the size of log file reaches the max size, the system will cut a half of the file. New logs will be retained. switch off : logs will remain, and the file size will increase gradually. default on, default size=1MB | |||
Verbose: | Asterisk console verbose message switch. | |||
Notice: | Asterisk console notice message switch. | |||
Warning: | Asterisk console warning message switch. | |||
Debug: | Asterisk console debug message switch. | |||
Error: | Asterisk console error message switch. | |||
DTMF: | Asterisk console DTMF info switch. | |||
Auto clean: (asterisk logs) | switch on : when the size of log file reaches the max size, the system will cut a half of the file. New logs will be retained. Switch off: logs will remain, and the file size will increase gradually. default on, default size=100KB2MB | |||
SIP Logs: | Whether enable or disable SIP log. | |||
Auto clean: (SIP logs) | switch on : when the size of log file reaches the max size, the system will cut a half of the file. New logs will be retained. Switch off: logs will remain, and the file size will increase gradually. default on, default size=2MB | |||
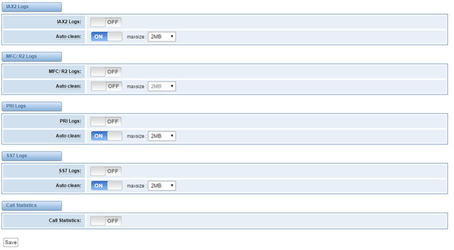
IAX2 Logs | Whether enable or disable IAX log | |||
Auto clean | switch on : when the size of log file reaches the max size, the system will cut a half of the file. New logs will be retained. Switch off: logs will remain, and the file size will increase gradually. default on, default size=2MB | |||
MFC/ R2 Logs | Whether enable or disable MFC/ R2 Logs log. | Auto cleanenable or disable MFC/ R2 Logs log. | ||
Auto clean | switch on : when the size of log file reaches the max size, the system will cut a half of the file. New logs will be retained. Switch off: logs will remain, and the file size will increase gradually. default on, default size=2MB | |||
PRI Logs | PRI port logs. You can choose one or more ports. If you choose "All", the "PRI" page will show you the logs about all the ports. | |||
Auto clean (PRI logs) | switch on : when the size of log file reaches the max size, the system will cut a half of the file. New logs will be retained. Switch off: logs will remain, and the file size will increase gradually. default on,default size= 100KB | |||
PRI Logs | PRI port logs. You can choose one or more ports. If you choose "All", the "PRI" page will show you the logs about all the ports. | |||
On the “Log Settings” page, you should set the related logs on to scan the responding logs page. For example, set “SIP Logs” on like the following, then you can turn to “SIP” page for sip logs, otherwise, sip logs is unavailable. And the same with other log pages. | ||||
.SS7 Logs | Whether enable or disable SS7 log | |||
Auto clean | switch on : when the size of log file reaches the max size, the system will cut a half of the file. New logs will be retained. Switch off: logs will remain, and the file size will increase gradually. default on, default size=2MB | |||
.SS7 Logs | Whether enable or disable SS7 log | |||
Auto clean | switch on : when the size of log file reaches the max size, the system will cut a half of the file. New logs will be retained. Switch off: logs will remain, and the file size will increase gradually. default on, default size=100KB | |||
Call Statistics | Whether enable or disable Call Statistics. | |||
System
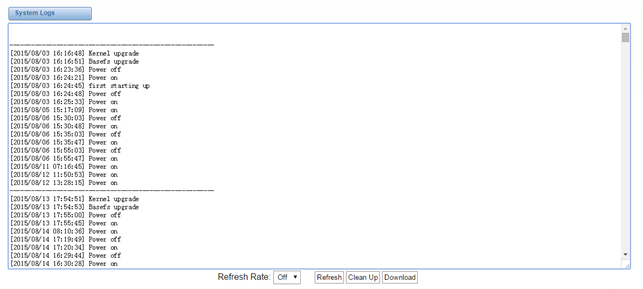
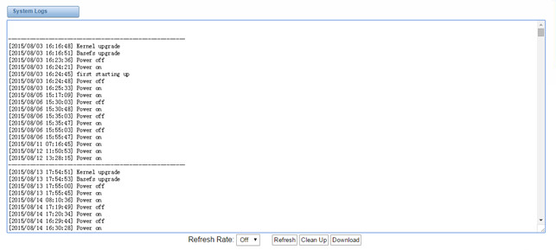
Figure 8-2-1 System Logs
Asterisk
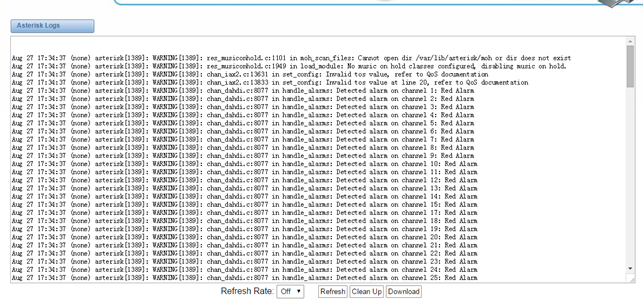
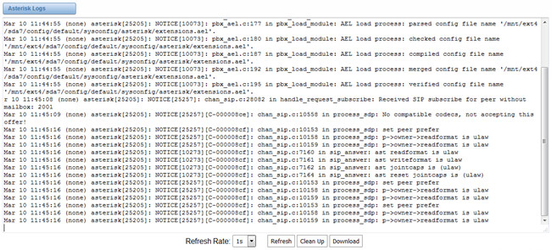
Figure 8-3-1 Asterisk Logs
On the pages of “system”, ”Asterisk”, “SIP”, “IAX2”, “SS7”, and “MFC/R2”, there are some functions: Displays the log by port, refresh regularly and log download.
Statistics
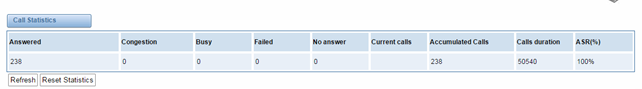
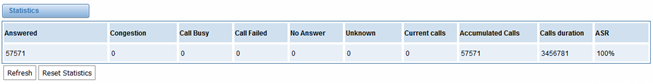
Figure 8-9-1 Call Statistics
...
gradually. default on, default size=2MB | ||
Call Statistics | Whether enable or disable Call Statistics. | |
8.2 System log
System log record every time power on, power off and firmware upgrade information.
Figure 8-2-1 System Log
8.3 Asterisk logs
On the pages of “Asterisk”, “SIP”, “IAX2”, “SS7”, “PRI” and “MFC/R2”, there owns the some functions—Displays the log by port, refresh regularly and log download.
Figure 8-3-1 Asterisk Log
8.4 Call Statistics
The figure of call statistics, you’ll find “Answered”, “congestion”, “Call busy”, “Call failed”, “No answer”, “Current calls”, “accumulated calls”, “Calls duration” and “ASR”. “ASR” stands for Answer Seizure Ratio. “Calls duration” will count the whole calls in the gateway. The call statistics will be saved before power off. It will be loaded after power on. It can be refreshed by itself. You can reset the statistics manually.
Figure 8-4-1 Call Statistics
Note: Do not forget to enable call statistics in “Log Setting” if you want to statistics the calls.
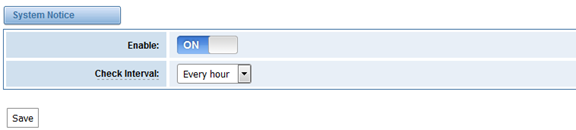
8.5 System Notice
The system notice could be generated by system to inform the network manager of what is going on if it has been enabled. Firmware upgrade messages from official website and auto provisioning messages from ACS are main notice right now. And at first, enable the system notice function like figure 8-5-1.
Figure 8-5-1 enable system notice function
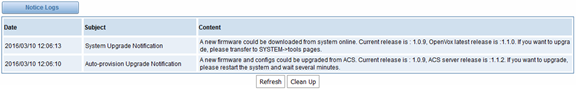
After about an hour, a system message is received in the web like 8-5-2.
Figure 8-5-2 enable system notice function
Note: Do not forget to enable system notice and check interval in “Log Setting” if you want to receive system messages.